Takotsubo stress cardiomyopathy following explantation of sEEG electrodes
- PMID: 33681668
- PMCID: PMC7918336
- DOI: 10.1002/epi4.12452
Takotsubo stress cardiomyopathy following explantation of sEEG electrodes
Abstract
Objective: Takotsubo stress cardiomyopathy is characterized by dysfunction of the left ventricle of the heart including apical ballooning and focal wall-motion abnormalities. Although reported in association with seizures and intracerebral hemorrhage, there are no studies reporting its occurrence in patients having stereoelectroencephalography (sEEG).
Methods: A 38-year-old lady with no prior history of cardiac disease experienced sudden onset chest pain and acute left ventricular failure 4 hours following explantation of stereoelectroencephalogram electrodes.
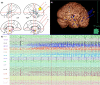
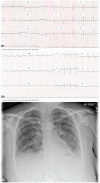
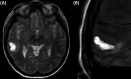
Results: A small parenchymal hematoma related to the right posterior temporal electrode had been noted postelectrode insertion but was asymptomatic. Focal-onset seizures from nondominant mesial temporal structures were recorded during sEEG. Following the presentation with LVF, new-onset anterolateral T-wave inversion with reciprocal changes in leads II, III, and aVF was noted on electrocardiogram (ECG) and the chest X-ray findings were consistent with pulmonary edema. Echocardiography demonstrated hypokinesis of the cardiac apex and septum consistent with Takotsubo stress cardiomyopathy.
Significance: Awareness of the possible complication of Takotsubo stress cardiomyopathy is required in an epilepsy surgery program.
Keywords: Takotsubo stress cardiomyopathy; intracerebral hemorrhage; stereoelectroencephalography.
© 2020 The Authors. Epilepsia Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to declare. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position of issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures
Comment in
-
Response: Implantation/explantation of sEEG electrodes and takotsubo syndrome: Plausible merits of additions to the protocol.Epilepsia Open. 2021 Jun;6(2):450-451. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12486. Epub 2021 May 12. Epilepsia Open. 2021. PMID: 34033233 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Implantation/explantation of sEEG electrodes and takotsubo syndrome: Plausible merits of some additions to the protocol.Epilepsia Open. 2021 Jun;6(2):449. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12487. Epub 2021 May 4. Epilepsia Open. 2021. PMID: 34033236 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ranieri M, Finsterer J, Bedini G, Parati EA, Bersano A. Takotsubo Syndrome: clinical features, pathogenesis, treatment, and relationship with cerebrovascular diseases. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2018;18(5):20. - PubMed
-
- Mullin JP, Shriver M, Alomar S, Najm I, Bulacio J, Chauvel P, et al. Is SEEG safe? A systematic review and meta‐analysis of stereo‐electroencephalography‐related complications. Epilepsia. 2016;57(3):386–401. - PubMed
-
- Stollberger C, Sauerberg M, Finsterer J. Immediate versus delayed detection of Takotsubo syndrome after epileptic seizures. J Neurol Sci. 2019;15(397):42–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

