Hepatic Stellate Cell Regulation of Liver Regeneration and Repair
- PMID: 33681672
- PMCID: PMC7917274
- DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1628
Hepatic Stellate Cell Regulation of Liver Regeneration and Repair
Abstract
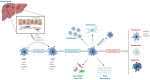
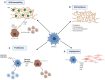
The hepatic mesenchyme has been studied extensively in the context of liver fibrosis; however, much less is known regarding the role of mesenchymal cells during liver regeneration. As our knowledge of the cellular and molecular mechanisms driving hepatic regeneration deepens, the key role of the mesenchymal compartment during the regenerative response has been increasingly appreciated. Single-cell genomics approaches have recently uncovered both spatial and functional zonation of the hepatic mesenchyme in homeostasis and following liver injury. Here we discuss how the use of preclinical models, from in vivo mouse models to organoid-based systems, are helping to shape our understanding of the role of the mesenchyme during liver regeneration, and how these approaches should facilitate the precise identification of highly targeted, pro-regenerative therapies for patients with liver disease.
© 2020 The Authors. Hepatology Communications published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Balabaud C, Bioulac‐Sage P, Desmouliere A. The role of hepatic stellate cells in liver regeneration. J Hepatol 2004;40:1023‐1026. - PubMed
-
- Williams R, Aspinall R, Bellis M, Camps‐Walsh G, Cramp M, Dhawan A, et al. Addressing liver disease in the UK: a blueprint for attaining excellence in health care and reducing premature mortality from lifestyle issues of excess consumption of alcohol, obesity, and viral hepatitis. Lancet 2017;384:1953‐1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

