Nucleic Acid Immunotherapeutics for Cancer
- PMID: 33681722
- PMCID: PMC7932307
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.0c00101
Nucleic Acid Immunotherapeutics for Cancer
Abstract
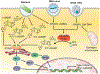
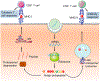
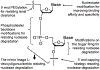
The past decade has witnessed the blossom of two fields: nucleic acid therapeutics and cancer immunotherapy. Unlike traditional small molecule medicines or protein biologics, nucleic acid therapeutics have characteristic features such as storing genetic information, immunomodulation, and easy conformational recovery. Immunotherapy uses the patients' own immune system to treat cancer. A variety of strategies have been developed for cancer immunotherapy including immune checkpoint blockade, adoptive cell transfer therapy, therapeutic vaccines, and oncolytic virotherapy. Interestingly, nucleic acid therapeutics have emerged as a pivotal class of regimen for cancer immunotherapy. Examples of such nucleic acid immunotherapeutics include immunostimulatory DNA/RNA, mRNA/plasmids that can be translated into immunotherapeutic proteins/peptides, and genome-editing nucleic acids. Like many other therapeutic nucleic acids, nucleic acid immunotherapeutics often require chemical modifications to protect them from enzymatic degradation and need drug delivery systems for optimal delivery to target tissues and cells and subcellular locations. In this review, we attempted to summarize recent advancement in the interfacial field of nucleic acid immunotherapeutics for cancer treatment.
Keywords: adjuvant; cancer; immunotherapy; nucleic acid therapeutics; vaccine.
Figures
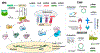

References
-
- Schuster M; Nechansky A; Kircheis R Cancer immunotherapy. Biotechnol. J 2006, 1 (2), 138–147. - PubMed
-
- Gabrilovich DI; Ishida T; Nadaf S; Ohm JE; Carbone DP Antibodies to Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Enhance the Efficacy of Cancer Immunotherapy by Improving Endogenous Dendritic Cell Function. Clin. Cancer Res 1999, 5 (10), 2963–2970. - PubMed
-
- Kwon ED; Foster BA; Hurwitz AA; Madias C; Allison JP; Greenberg NM; Burg MB Elimination of residual metastatic prostate cancer after surgery and adjunctive cytotoxic T lymphocyteassociated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) blockade immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 1999, 96 (26), 15074–15079. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yee C; Thompson JA; Byrd D; Riddell SR; Roche P; Celis E; Greenberg PD Adoptive T cell therapy using antigen-specific CD8+ T cell clones for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma: in vivo persistence, migration, and antitumor effect of transferred T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2002, 99 (25), 16168–16173. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
