Latent rheumatic, thyroid and phospholipid autoimmunity in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 33681751
- PMCID: PMC7920824
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100091
Latent rheumatic, thyroid and phospholipid autoimmunity in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
Abstract
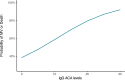
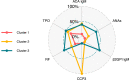
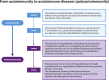
Autoimmune responses mediated by autoantibodies have been observed in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Herein, we evaluate the presence of rheumatic, thyroid and phospholipid autoantibodies in sera samples from 120 adult hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in comparison to pre-pandemic samples from 100 healthy individuals. In addition, to estimate the frequency of these autoantibodies in COVID-19, a meta-analysis of selected articles was conducted. Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 had latent autoimmunity characterized by a high frequency of anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies, rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide third generation antibodies, antinuclear antibodies (ANAs), IgM anti-β2-glycoprotein I (β2GP1) and IgM anti-cardiolipin antibodies. The meta-analysis confirmed our results, with RF and ANAs being the most common autoantibodies. In addition, cluster analysis revealed that those patients with high frequency of RF, IgM anti-β2GP1 antibodies and ANAs had a longer hospital stay, required more vasopressors during hospitalization, and were more likely to develop critical disease. These data suggest that latent autoimmunity influences the severity of COVID-19, and support further post-COVID studies in order to evaluate the development of overt autoimmunity.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; COVID-19; Clusters; Latent autoimmunity; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Rodríguez Y., Novelli L., Rojas M., De Santis M., Acosta-Ampudia Y., Monsalve D.M., Ramírez-Santana C., Costanzo A., Ridgway W.M., Ansari A.A., Gershwin M.E., Selmi C., Anaya J.-M. Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19. J. Autoimmun. 2020;114:102506. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102506. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou Y., Han T., Chen J., Hou C., Hua L., He S., Guo Y., Zhang S., Wang Y., Yuan J., Zhao C., Zhang J., Jia Q., Zuo X., Li J., Wang L., Cao Q., Jia E. Clinical and autoimmune characteristics of severe and critical cases of COVID-19. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020;13:1077–1086. doi: 10.1111/cts.12805. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schiaffino M.T., Di Natale M., García-Martínez E., Navarro J., Muñoz-Blanco J.L., Demelo-Rodríguez P., Sánchez-Mateos P. Immunoserologic detection and diagnostic relevance of cross-reactive autoantibodies in coronavirus disease 2019 patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2020;222:1439–1443. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa485. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borghi M.O., Beltagy A., Garrafa E., Curreli D., Cecchini G., Bodio C., Grossi C., Blengino S., Tincani A., Franceschini F., Andreoli L., Lazzaroni M.G., Piantoni S., Masneri S., Crisafulli F., Brugnoni D., Muiesan M.L., Salvetti M., Parati G., Torresani E., Mahler M., Heilbron F., Pregnolato F., Pengo M., Tedesco F., Pozzi N., Meroni P.L. Anti-phospholipid antibodies in COVID-19 are different from those detectable in the anti-phospholipid syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:2692. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584241. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

