The effects of cognitive-behavioral group therapy for reducing symptoms of internet addiction disorder and promoting quality of life and mental health
- PMID: 33681908
- PMCID: PMC7932042
- DOI: 10.47626/2237-6089-2020-0010
The effects of cognitive-behavioral group therapy for reducing symptoms of internet addiction disorder and promoting quality of life and mental health
Abstract
Introduction: Internet addiction disorder has reportedly become an important cause of health and social problems. The aim of this study was to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral group therapy for internet addiction symptoms, quality of life, and mental health of students with internet addiction.
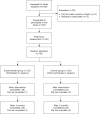
Methods: This was a quasi-experimental study with pretest-posttest measures and a control group. The statistical population of the study consisted of all students at Tehran universities in the academic year of 2018-19. The target group was selected through an internet addiction test and a clinical interview using a targeted sampling method and was divided into experimental and control groups by randomization. The experimental group participated in fifteen 90-minute cognitive-behavioral group therapy sessions. Before, immediately after, and 3 months after the treatment, the internet addiction symptoms of both groups were evaluated to assess mental health with the IAT, quality of life (QOL), and SCL-90-R questionnaires. Data were analyzed with ANCOVA analysis using SPSS Statistics 20 software.
Results: After treatment, cognitive-behavioral therapy groups showed reductions in internet addiction scores (p < 0.05). Results showed that the cognitive-behavioral group therapy was effective for improving quality of life (p < 0.05) and mental illnesses (p < 0.05) in students with internet addiction.
Conclusions: Cognitive-behavioral group therapy can enhance awareness and mental health of students with internet addiction. Therefore, this intervention can be used as a beneficial treatment to reduce internet addiction symptoms and improve the condition of people with behavioral addictions such as internet dependency.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
No conflicts of interest declared concerning the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of internet addiction and academic resilience in predicting the mental health of high school students in Tehran.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 4;24(1):420. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05853-6. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38834960 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of educational intervention based on BASNEF model for reducing internet addiction among female students: a quasi-experimental study.Ital J Pediatr. 2019 Dec 19;45(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s13052-019-0761-4. Ital J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31856869 Free PMC article.
-
Web-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Female Patients With Eating Disorders: Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2015 Jun 18;17(6):e152. doi: 10.2196/jmir.3946. J Med Internet Res. 2015. PMID: 26088580 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Educational intervention for the prevention of internet addiction disorder among 15-19-year-old adolescents in Colombo district, Sri Lanka.Ceylon Med J. 2022 Dec 31;67(4):131-137. doi: 10.4038/cmj.v67i4.9740. Ceylon Med J. 2022. PMID: 38421241 Review.
-
Treatments of internet gaming disorder: a systematic review of the evidence.Expert Rev Neurother. 2020 Jan;20(1):85-93. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2020.1671824. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Expert Rev Neurother. 2020. PMID: 31544539 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological Interventions on Gaming Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Psychiatry Investig. 2025 May;22(5):490-503. doi: 10.30773/pi.2024.0358. Epub 2025 May 15. Psychiatry Investig. 2025. PMID: 40404379 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise and psychological interventions on smartphone addiction among university students: A systematic review.Front Psychol. 2022 Oct 5;13:1021285. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1021285. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36275318 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of generalized anxiety and social anxiety symptoms with sleep duration, amount of intense exercise, and excessive internet use among adolescents.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 12;24(1):791. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06231-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39533195 Free PMC article.
-
Internet Addiction Management: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Interventions and Modalities.Cureus. 2024 Mar 4;16(3):e55466. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55466. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38571828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substance and Behavioral Addictions, and Their Consequences among Vulnerable Populations.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 19;19(10):6163. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19106163. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35627700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- . Poorolajal J, Mohammadi Y, Soltanian AR, Ahmadpoor J. The top six risky behaviors among Iranian university students: a national survey. J Public Health (Oxf). 2019;41:788-797 - PubMed
-
- . Doosti Irani A, Beagheri Amiri F, Khajekazemi R, Mostafavi R. Prevalence of Internet addiction among students and graduates of epidemiology, clinical science and basic sciences in Iran: a cross sectional study. Iran J Epidemiol. 2017;13:14-21.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous