Value of HMGB1 expression for assessing gastric cancer severity: a systematic meta-analysis
- PMID: 33682495
- PMCID: PMC7944546
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060521993312
Value of HMGB1 expression for assessing gastric cancer severity: a systematic meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the clinical value of high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) expression levels in patients with gastric cancer.
Methods: Articles published from January 2000 to August 2022 were searched using PubMed, Google Scholar and Science Direct, Springer, Wiley and NIH to evaluate the clinicopathological significance of HMGB1 expression in gastric cancer.
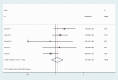
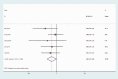
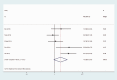
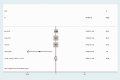
Results: A total of 156 publications were selected, of which six studies, comprising 846 patients, met the criteria for inclusion in this study. Forest plots of clinicopathological characteristics indicated that HMGB1 expression was not associated with age (odds ratio (OR) = 1.07, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.89-1.28), sex (OR = 0.90, 95% CI: 0.81-1.00), TNM (OR = 1.39, 95% CI: 0.82-2.37), N stage (OR = 1.42, 95% CI: 0.97-2.07), or tumor differentiation (OR = 0.96, 95% CI: 0.71-1.29), but was highly correlated with pT stage (OR = 1.56, 95% CI: 1.17-2.07). Funnel plots showed no significant publication bias in the included studies in terms of age, sex, TNM, pT stage, N stage, or tumor differentiation.
Conclusion: HMGB1 expression was significantly correlated with tumor pT stage, but not with age, sex, TNM stage, tumor N stage, tumor differentiation, or lymphatic metastasis in patients with GC.
Keywords: Forest plot; Gastric cancer; HMGB1; pT stage; prognosis; tumor stage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures








Similar articles
-
Double-positive expression of high-mobility group box 1 and vascular endothelial growth factor C indicates a poorer prognosis in gastric cancer patients.World J Surg Oncol. 2013 Jul 18;11:161. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-11-161. World J Surg Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23866030 Free PMC article.
-
High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) expression in gastric adenocarcinomas.J BUON. 2018 Mar-Apr;23(2):422-427. J BUON. 2018. PMID: 29745087
-
HIF1A protein expression is correlated with clinical features in gastric cancer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 14;14(1):13736. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63019-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38877062 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological Significance of Neuropilin 1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Dis Markers. 2020 Sep 19;2020:4763492. doi: 10.1155/2020/4763492. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 33014187 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical significance of snail protein expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.Hum Genomics. 2016 Jul 25;10 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):22. doi: 10.1186/s40246-016-0070-6. Hum Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27461247 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Contributions of the receptor for advanced glycation end products axis activation in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Feb 14;29(6):997-1010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i6.997. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36844144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

