Local genetic context shapes the function of a gene regulatory network
- PMID: 33683203
- PMCID: PMC7968929
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.65993
Local genetic context shapes the function of a gene regulatory network
Abstract
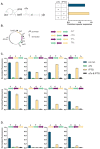
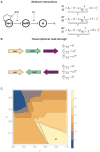
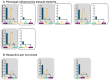
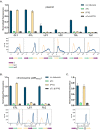
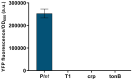
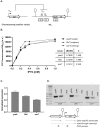
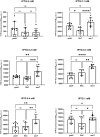
Gene expression levels are influenced by multiple coexisting molecular mechanisms. Some of these interactions such as those of transcription factors and promoters have been studied extensively. However, predicting phenotypes of gene regulatory networks (GRNs) remains a major challenge. Here, we use a well-defined synthetic GRN to study in Escherichia coli how network phenotypes depend on local genetic context, i.e. the genetic neighborhood of a transcription factor and its relative position. We show that one GRN with fixed topology can display not only quantitatively but also qualitatively different phenotypes, depending solely on the local genetic context of its components. Transcriptional read-through is the main molecular mechanism that places one transcriptional unit (TU) within two separate regulons without the need for complex regulatory sequences. We propose that relative order of individual TUs, with its potential for combinatorial complexity, plays an important role in shaping phenotypes of GRNs.
Keywords: E. coli; chromosomes; computational biology; gene expression; genetic context; genotype phenotype map; systems biology.
© 2021, Nagy-Staron et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AN, KT, CC, ES, BK, TP, CG No competing interests declared
Figures



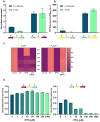
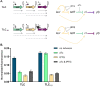
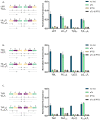
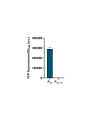



Similar articles
-
Inference of Gene Regulatory Network Based on Local Bayesian Networks.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Aug 1;12(8):e1005024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005024. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27479082 Free PMC article.
-
Feedbacks from the metabolic network to the genetic network reveal regulatory modules in E. coli and B. subtilis.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 4;13(10):e0203311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203311. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30286091 Free PMC article.
-
GreA and GreB Enhance Expression of Escherichia coli RNA Polymerase Promoters in a Reconstituted Transcription-Translation System.ACS Synth Biol. 2016 Sep 16;5(9):929-35. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00017. Epub 2016 May 19. ACS Synth Biol. 2016. PMID: 27186988
-
Gene-centered regulatory networks.Brief Funct Genomics. 2010 Jan;9(1):4-12. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elp049. Epub 2009 Dec 13. Brief Funct Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20008400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From plant gene regulatory grids to network dynamics.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 May;1819(5):454-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.016. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22406342 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular basis for lethal cross-talk between two unrelated bacterial transcription factors - the regulatory protein of a restriction-modification system and the repressor of a defective prophage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 28;50(19):10964-10980. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac914. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36271797 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Design of Robust Genetic Circuits: Structural Variants and Parameter Uncertainty.ACS Synth Biol. 2021 Dec 17;10(12):3316-3329. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00193. Epub 2021 Nov 22. ACS Synth Biol. 2021. PMID: 34807573 Free PMC article.
-
DNA supercoiling in bacteria: state of play and challenges from a viewpoint of physics based modeling.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 30;14:1192831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1192831. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37965550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inference of differential gene regulatory networks using boosted differential trees.Bioinform Adv. 2024 Feb 29;4(1):vbae034. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbae034. eCollection 2024. Bioinform Adv. 2024. PMID: 38505804 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing the scale of synthetic biology via cross-species transfer of cellular functions enabled by iModulon engraftment.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 15;15(1):2356. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46486-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38490991 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

