A One Health Approach to Child Stunting: Evidence and Research Agenda
- PMID: 33684062
- PMCID: PMC8103449
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-1129
A One Health Approach to Child Stunting: Evidence and Research Agenda
Abstract
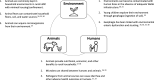
Stunting (low height for age) affects approximately one-quarter of children aged < 5 years worldwide. Given the limited impact of current interventions for stunting, new multisectoral evidence-based approaches are needed to decrease the burden of stunting in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Recognizing that the health of people, animals, and the environment are connected, we present the rationale and research agenda for considering a One Health approach to child stunting. We contend that a One Health strategy may uncover new approaches to tackling child stunting by addressing several interdependent factors that prevent children from thriving in LMICs, and that coordinated interventions among human health, animal health, and environmental health sectors may have a synergistic effect in stunting reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclaimer: The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of their institutions.
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF, World Health Organization, World Bank Group , 2017. Levels and Trends in Child Malnutrition in UNICEF/WHO/World Bank Group Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates Key Findings of the 2016 Edition. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO.
-
- Bhutta ZA, Das JK, Rizvi A, Gaffey MF, Walker N, Horton S, Webb P, Lartey A, Black RE, 2013. Evidence-based interventions for improvement of maternal and child nutrition: what can be done and at what cost? Lancet 382: 452–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical