Genotypes and phylogenetic analysis of adenovirus in children with respiratory infection in Buenos Aires, Argentina (2000-2018)
- PMID: 33684131
- PMCID: PMC7939361
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248191
Genotypes and phylogenetic analysis of adenovirus in children with respiratory infection in Buenos Aires, Argentina (2000-2018)
Abstract
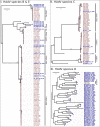
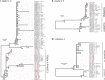
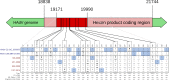
Human adenoviruses (HAdV) are one of the most frequent causes of respiratory infections around the world, causing mild to severe disease. In Argentina, many studies focused on the association of HAdV respiratory infection with severe disease and fatal outcomes leading to the discovery in 1984 of a genomic variant 7h associated with high fatality. Although several molecular studies reported the presence of at least 4 HAdV species (B, C, D and E) in Argentina, few sequences were available in the databases. In this study, sequences from the hexon gene region were obtained from 141 patients as a first approach to assess the genetic diversity of HAdVs circulating in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Phylogenetic analysis of these sequences and others recovered from public databases confirmed the circulation of the four above-mentioned species represented by 11 genotypes, with predominance in species B and C and shifts in their proportion in the studied period (2000 to 2018). The variants detected in Argentina, for most of the genotypes, were similar to those already described in other countries. However, uncommon lineages belonging to genotypes C2, C5 and E4 were detected, which might indicate the circulation of local variants and will deserve further studies of whole-genome sequences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Echavarría M, Maldonado D, Elbert G, Videla C, Rappaport R, Carballal G. Use of PCR to demonstrate presence of adenovirus species B, C, or F as well as coinfection with two adenovirus species in children with flu-like symptoms. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;44: 625–627. 10.1128/JCM.44.2.625–627.2006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

