Paternal genetic variants and risk of obstructive heart defects: A parent-of-origin approach
- PMID: 33684136
- PMCID: PMC7971842
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009413
Paternal genetic variants and risk of obstructive heart defects: A parent-of-origin approach
Abstract
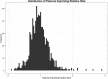
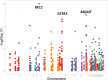
Previous research on risk factors for obstructive heart defects (OHDs) focused on maternal and infant genetic variants, prenatal environmental exposures, and their potential interaction effects. Less is known about the role of paternal genetic variants or environmental exposures and risk of OHDs. We examined parent-of-origin effects in transmission of alleles in the folate, homocysteine, or transsulfuration pathway genes on OHD occurrence in offspring. We used data on 569 families of liveborn infants with OHDs born between October 1997 and August 2008 from the National Birth Defects Prevention Study to conduct a family-based case-only study. Maternal, paternal, and infant DNA were genotyped using an Illumina Golden Gate custom single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) panel. Relative risks (RR), 95% confidence interval (CI), and likelihood ratio tests from log-linear models were used to estimate the parent-of-origin effect of 877 SNPs in 60 candidate genes in the folate, homocysteine, and transsulfuration pathways on the risk of OHDs. Bonferroni correction was applied for multiple testing. We identified 3 SNPs in the transsulfuration pathway and 1 SNP in the folate pathway that were statistically significant after Bonferroni correction. Among infants who inherited paternally-derived copies of the G allele for rs6812588 in the RFC1 gene, the G allele for rs1762430 in the MGMT gene, and the A allele for rs9296695 and rs4712023 in the GSTA3 gene, RRs for OHD were 0.11 (95% CI: 0.04, 0.29, P = 9.16x10-7), 0.30 (95% CI: 0.17, 0.53, P = 9.80x10-6), 0.34 (95% CI: 0.20, 0.57, P = 2.28x10-5), and 0.34 (95% CI: 0.20, 0.58, P = 3.77x10-5), respectively, compared to infants who inherited maternally-derived copies of the same alleles. We observed statistically significant decreased risk of OHDs among infants who inherited paternal gene variants involved in folate and transsulfuration pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CC/CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DD001223/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- U54 TR001629/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- EP-D-18-001/EPA/EPA/United States
- U01 DD001285/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DD001224/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DD001039/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DD001227/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- P30 ES030285/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD039054/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DD001229/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- CDP 13-003/HX/HSRD VA/United States
- U01 DD001306/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DD001226/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

