Trends in overdose experiences and prevention behaviors among people who use opioids in Baltimore, MD, 2017-2019
- PMID: 33684772
- PMCID: PMC8590734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108650
Trends in overdose experiences and prevention behaviors among people who use opioids in Baltimore, MD, 2017-2019
Abstract
Background: Little is known about trends in overdose behaviors. This study explored non-fatal overdose and engagement in overdose prevention behaviors and compared these trends to city-wide overdose fatality rates from 2017 to 2019 in Baltimore, MD.
Methods: The analysis included people who used opioids (PWUO; N = 502) recruited through a community-based study. Enrollment date was used to categorize participants into annual quarters. Logistic regression models examined change in overdose experiences and prevention behaviors with time. Baltimore's fatal overdoses were also mapped over the study period to assess overlaps in trends.
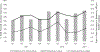
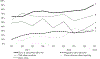
Results: The majority of the sample were male(68 %), Black(61 %), reported past 6 months homelessness(56 %), and were on average 45 years old. Most had witnessed(61 %), and 28 % had personally experienced an overdose in the past 6 months. Witnessing overdose marginally increased(aβ = 0.182;p = 0.058) while experiencing overdose did not significantly change by enrollment quarter. Most participants had or had been prescribed naloxone(72 %), and one fifth(22 %) regularly carried naloxone, with both access to(aβ = 0,408;p = 0.002) and carrying naloxone(aβ = 0.302;p = 0.006) increasing over time. Overdose communication remained stable, with 63 % of participants reporting discussing overdose sometimes/often. Among participants who injected (n = 376), regularly injecting alone decreased(aβ=-0.207;p = 0.055), and reporting others often/always having naloxone with them when injecting increased over time(aβ = 0.573;p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Witnessed overdose marginally increased from 2017 to 2019, aligning with city trends of fatal overdose. Overdose prevention behaviors significantly increased over time. Despite reporting having naloxone or a naloxone prescription, most PWUO did not regularly carry naloxone, and many used alone. Social network diffusion interventions may be a strategy to promote normative overdose prevention behaviors.
Keywords: Harm reduction; Naloxone; Overdose prevention; People who use opioids.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Baltimore City Health Department. (2020a). Baltimore City’s Response to the Opioid Epidemic. Retrieved June 1, 2020, from https://health.baltimorecity.gov/opioid-overdose/baltimorecity-overdose-...
-
- Baltimore City Health Department. (2020b). Fighting stigma with education. Retrieved July 12, 2020, from https://health.baltimorecity.gov/fighting-stigma-education
-
- Baltimore City Health Department. (2020c). Naloxone. Retrieved June 1, 2020, from https://health.baltimorecity.gov/naloxone
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

