Down-Regulation of TMPO-AS1 Induces Apoptosis in Lung Carcinoma Cells by Regulating miR-143-3p/CDK1 Axis
- PMID: 33685293
- PMCID: PMC8093611
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033820948880
Down-Regulation of TMPO-AS1 Induces Apoptosis in Lung Carcinoma Cells by Regulating miR-143-3p/CDK1 Axis
Abstract
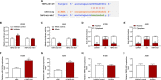
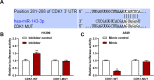
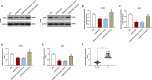
Evidence has shown that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) play pivotal roles in cancer promotion as well as suppression. But the molecular mechanism of lncRNA TMPO antisense transcript 1 (TMPO-AS1) in lung cancer (LC) remains unclear. This study mainly investigated the effect of TMPO-AS1 in LC treatment. TMPO-AS1 was tested by Kaplan-Meier method. Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was employed to assess the expressions of TMPO-AS1, miR-143-3p, and CDK1 respectively in LC tissues and cell lines. TMPO-AS1, miR-143-3p and CDK1 expressions in LC cells were regulated through cell transfection, followed by MTT for cell viability detection. Besides, dual-luciferase reporter assays were performed to verify the interrelated microRNA of TMPO-AS1 and the target of miR-143-3p. Western blot experiments were used to examine the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins, and flow cytometry tested the cell apoptosis in treated cells. TMPO-AS1 and CDK1 were overexpressed in LC tissues and cells, while miR-143-3p level was suppressed. The decrease of TMPO-AS1 led to the increase of miR-143-3p, which further resulted in the reduction of CDK1. Down-regulating TMPO-AS1 reduced LC cell viability, motivated cell apoptosis, as well as promoted the expressions of Bcl and CCND1 and restrained Caspase-3 level, but all these consequences were abrogated by miR-143-3p inhibitor. Simultaneously, siCDK1 could reverse the anti-apoptosis and pro-activity functions of miR-143-3p inhibitor in LC cells. Down-regulation of TMPO-AS1 has the effects of pro-apoptosis in LC by manipulating miR-143-3p/CDK1, which is hopeful to be a novel therapy for LC patients.
Keywords: TMPO antisense transcript 1; cyclin-dependent kinase 1; lung cancer; miR-143-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Faure M. Lung cancer in Europe: turning the spotlight on the biggest cancer killer. Eur Respir J. 2016;47(1):42–44 doi:10.1183/13993003.01495-2015 - PubMed
-
- Nanavaty P, Alvarez MS, Alberts WM. Lung cancer screening: advantages, controversies, and applications. Cancer Control. 2014;21(1):9–14 doi:10.1177/107327481402100102 - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Canales J, Parra-Cuentas E, Wistuba II. Diagnosis and molecular classification of lung cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2016;170:25–46 doi:10.1007/978-3-319-40389-2_2 - PubMed
-
- Zheng M. Classification and pathology of lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25(3):447–468. doi:10.1016/j.soc.2016.02.003 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

