In-vitro glistening formation in six different foldable hydrophobic intraocular lenses
- PMID: 33685428
- PMCID: PMC7938589
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-021-01879-6
In-vitro glistening formation in six different foldable hydrophobic intraocular lenses
Abstract
Background: Glistenings describe small, refractile microvacuoles that may arise within the intraocular lens (IOL) material and reduce the patients' quality of vision. Lenses composed of hydrophobic acrylic material are particularly affected by glistening formation. In this study, we compared the tendency of glistening formation in six different types of hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses (IOLs).
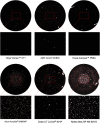
Methods: We used a well-established accelerated laboratory method to develop glistenings in the following IOLs: Vivinex XY1 (Hoya), AcrySof SN60WF (Alcon), Tecnis ZCB00 (AMO), Avansee PN6A (Kowa), Aktis SP NS-60YG (Nidek), and CT Lucia 601P (Zeiss). IOLs were first immersed in saline at 45 °C for 24 h and then at 37 °C for 2.5 h in a water bath. Microvacuole (MV) density and size (Miyata grading) were documented and calculated using an image analysis program.
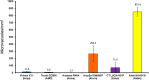
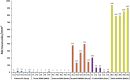
Results: The mean glistening density [MV/mm2] and mean Miyata grading (in brackets) were: Vivinex: 11.6 ± 5.7 (0), SN60WF: 264.4 ± 110.3 (2.6), Tecnis: 6.0 ± 2.8 (0), Avansee: 2.2 ± 0.7 (0), Aktis: 851.4 ± 59.4 (3+) and CT Lucia: 71.0 ± 71.6 (1).
Conclusions: While all tested IOLs showed glistenings with the accelerated laboratory method, the Aktis and SN60WF showed the highest microvacuole density, followed by the CT Lucia. In comparison, the Vivinex, Tecnis, and Avansee IOLs showed far fewer number of glistenings.
Conflict of interest statement
GUA and RK received research grants from Alcon, Kowa, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Hoya, Bausch&Lomb, Ophthec, Physiol, Powervision, Rayner, SIFI, Johnson&Johnson, Acufocus, and Oculentis. TT, PM, and CYC received research grants from Hoya, Alcon, Bausch&Lomb, and Kowa. HSS has no competing interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Kanclerz P, Yildirim TM, Khoramnia R. Microscopic Characteristics of Late Intraocular Lens Opacifications. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

