Recurrent and acute abdominal pain as the main clinical manifestation in patients with hereditary angioedema
- PMID: 33685557
- PMCID: PMC8133019
- DOI: 10.2500/aap.2021.42.210001
Recurrent and acute abdominal pain as the main clinical manifestation in patients with hereditary angioedema
Abstract
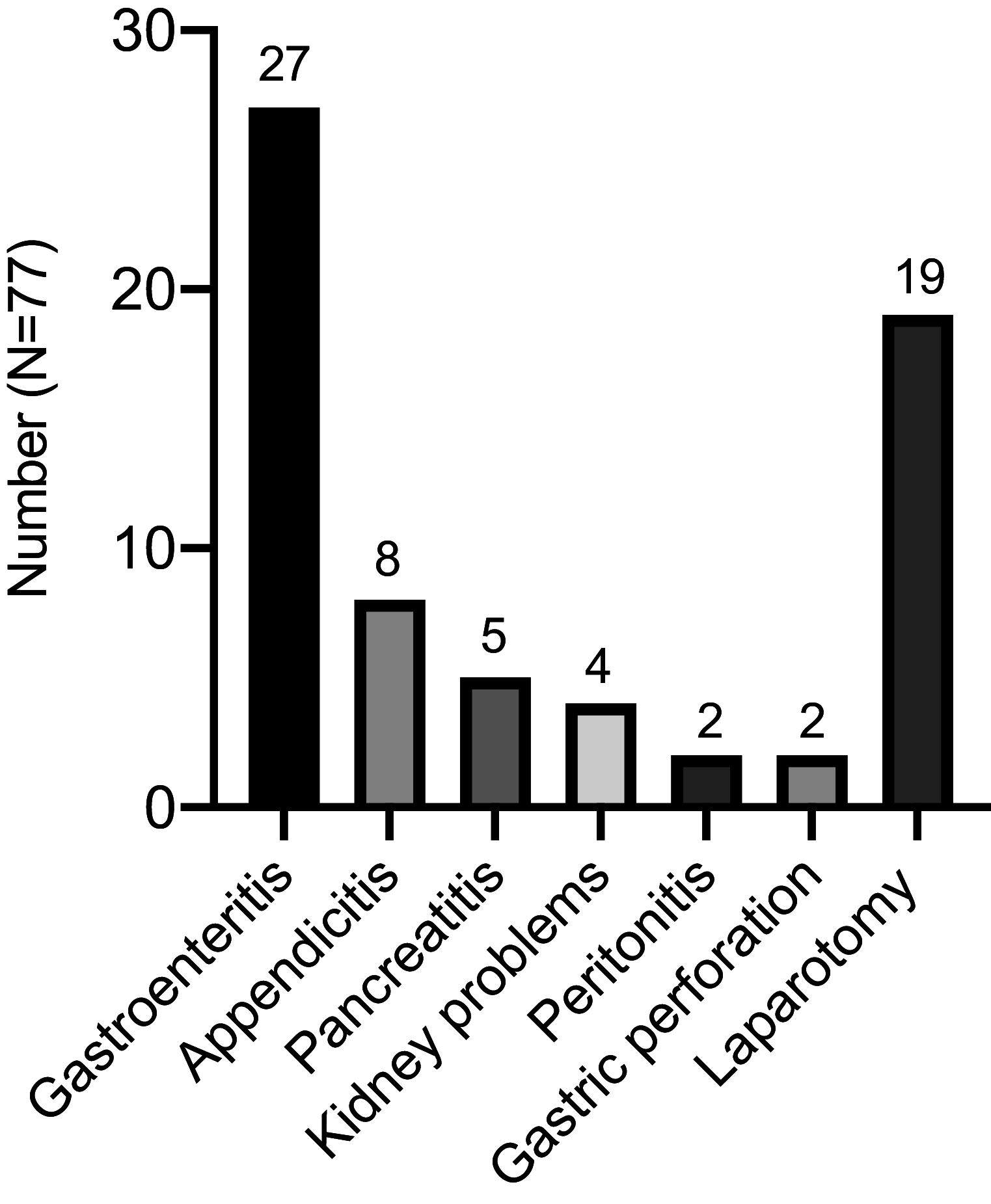
Background: Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a rare disease that often leads to misdiagnosis. The delay of diagnosis is > 10 years in China. Recurrent and acute abdominal pain is one of the common symptoms of HAE. Because of the high misdiagnosis rate, it usually results in unnecessary surgical procedures. This study focused on the clinical symptoms and management of HAE-related abdominal attacks in Chinese patients to provide some new insight for the emergency department (ED) physicians and gastroenterologists. Methods: A Web-based survey was conducted among 107 patients with HAE from 94 unrelated families. Detailed questions with respect to the abdominal attacks were asked, including the frequency, symptoms, and duration before and after confirmed diagnosis. The demographic characteristics, diagnosis process, and treatment outcomes were also included. Results: Approximately 70% of the patients with HAE presented with abdominal symptoms during the onset of edema, mostly characterized by pain (94.8%), nausea (83.1%), vomiting (83.1%), diarrhea (59.7%), and constipation (23.4%). The patients were easily misdiagnosed as having gastroenteritis (35.1%) and appendicitis (10.4%), and 24.7% of them received unnecessary appendectomy or laparotomy. Danazol, a widely used drug for long-term prophylaxis of HAE in China, can reduce the attack frequency and alleviate the abdominal symptoms, but the adverse effects are also significant and more severe in women. Conclusions: Abdominal symptoms are common and important clinical features of HAE but are easily confused with other gastrointestinal diseases. ED physicians and gastroenterologists should consider HAE when patients experience recurrent and unexplained abdominal pain. Proper medical treatment should be administered in a timely manner if an HAE diagnosis is confirmed and efforts are required to increase access in China to medications both for on-demand treatment and long-term prophylaxis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare pertaining to this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consider Hereditary Angioedema in the Differential Diagnosis for Unexplained Recurring Abdominal Pain.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2022 Oct 1;56(9):740-747. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001744. Epub 2022 Aug 15. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35960533 Free PMC article.
-
Many faces of angioedema: focus on the diagnosis and management of abdominal manifestations of hereditary angioedema.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Apr;24(4):353-61. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283517998. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22410711 Review.
-
Leukocytosis and high hematocrit levels during abdominal attacks of hereditary angioedema.BMC Gastroenterol. 2013 Aug 2;13:123. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-13-123. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23915279 Free PMC article.
-
Angioedema with severe acute abdominal pain: Think of hereditary angioedema.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2021 Jul;45(4):101702. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2021.101702. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33864899
-
The importance of recognizing and managing a rare form of angioedema: hereditary angioedema due to C1-inhibitor deficiency.Postgrad Med. 2021 Aug;133(6):639-650. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2021.1905364. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Postgrad Med. 2021. PMID: 33993830 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiology, economic, and humanistic burden of hereditary angioedema: a systematic review.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Jul 8;19(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03265-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 38978028 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary angioedema again revisited.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021 Mar 1;42(2):105-107. doi: 10.2500/aap.2021.42.210009. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021. PMID: 33685554 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The multifactorial impact of receiving a hereditary angioedema diagnosis.World Allergy Organ J. 2023 Jun 30;16(6):100792. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2023.100792. eCollection 2023 Jun. World Allergy Organ J. 2023. PMID: 37448849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proactive identification of rare diseases: lessons from hereditary angioedema diagnosis using electronic medical records.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Jul 28;20(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03882-2. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40722186 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary Angioedema: Diagnostic Algorithm and Current Treatment Concepts.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021 Nov 22;12(6):796-804. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_398_21. eCollection 2021 Nov-Dec. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021. PMID: 34934714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zuraw BL. Clinical practice. Hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1027–1036. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Xu Y, Liu Y, et al. . Hereditary angioedema: a Chinese perspective. Eur J Dermatol. 2019; 29:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Wang X, Xu Y, et al. . Risk factors for diagnostic delay in Chinese patients with hereditary angioedema. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019; 40:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Walford HH, Zuraw BL. Current update on cellular and molecular mechanisms of hereditary angioedema. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 112:413–418. - PubMed
-
- Csuka D, Veszeli N, Varga L, et al. . The role of the complement system in hereditary angioedema. Mol Immunol. 2017; 89:59–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical