Spectrum of Mechanisms of Resistance to Crizotinib and Lorlatinib in ROS1 Fusion-Positive Lung Cancer
- PMID: 33685866
- PMCID: PMC8127383
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0032
Spectrum of Mechanisms of Resistance to Crizotinib and Lorlatinib in ROS1 Fusion-Positive Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Current standard initial therapy for advanced, ROS proto-oncogene 1, receptor tyrosine kinase fusion (ROS1)-positive (ROS1+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is crizotinib or entrectinib. Lorlatinib, a next-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase/ROS1 inhibitor, recently demonstrated efficacy in ROS1+ NSCLC, including in crizotinib-pretreated patients. However, mechanisms of lorlatinib resistance in ROS1+ disease remain poorly understood. Here, we assessed mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib and lorlatinib.
Experimental design: Biopsies from patients with ROS1 + NSCLC progressing on crizotinib or lorlatinib were profiled by genetic sequencing.
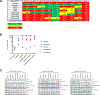
Results: From 55 patients, 47 post-crizotinib and 32 post-lorlatinib biopsies were assessed. Among 42 post-crizotinib and 28 post-lorlatinib biopsies analyzed at distinct timepoints, ROS1 mutations were identified in 38% and 46%, respectively. ROS1 G2032R was the most commonly occurring mutation in approximately one third of cases. Additional ROS1 mutations included D2033N (2.4%) and S1986F (2.4%) post-crizotinib and L2086F (3.6%), G2032R/L2086F (3.6%), G2032R/S1986F/L2086F (3.6%), and S1986F/L2000V (3.6%) post-lorlatinib. Structural modeling predicted ROS1L2086F causes steric interference to lorlatinib, crizotinib, and entrectinib, while it may accommodate cabozantinib. In Ba/F3 models, ROS1L2086F, ROS1G2032R/L2086F, and ROS1S1986F/G2032R/L2086F were refractory to lorlatinib but sensitive to cabozantinib. A patient with disease progression on crizotinib and lorlatinib and ROS1 L2086F received cabozantinib for nearly 11 months with disease control. Among lorlatinib-resistant biopsies, we also identified MET amplification (4%), KRAS G12C (4%), KRAS amplification (4%), NRAS mutation (4%), and MAP2K1 mutation (4%).
Conclusions: ROS1 mutations mediate resistance to crizotinib and lorlatinib in more than one third of cases, underscoring the importance of developing next-generation ROS1 inhibitors with potency against these mutations, including G2032R and L2086F. Continued efforts are needed to elucidate ROS1-independent resistance mechanisms.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
Figures




References
-
- Michels S, Massuti B, Schildhaus HU, Franklin J, Sebastian M, Felip E et al. Safety and Efficacy of Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced or Metastatic ROS1-Rearranged Lung Cancer (EUCROSS): A European Phase II Clinical Trial. J Thorac Oncol 2019;14(7):1266–76 doi 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.03.020. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

