Genomic insights into the host specific adaptation of the Pneumocystis genus
- PMID: 33686174
- PMCID: PMC7940399
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01799-7
Genomic insights into the host specific adaptation of the Pneumocystis genus
Abstract
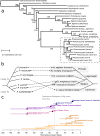
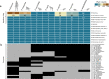
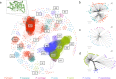
Pneumocystis jirovecii, the fungal agent of human Pneumocystis pneumonia, is closely related to macaque Pneumocystis. Little is known about other Pneumocystis species in distantly related mammals, none of which are capable of establishing infection in humans. The molecular basis of host specificity in Pneumocystis remains unknown as experiments are limited due to an inability to culture any species in vitro. To explore Pneumocystis evolutionary adaptations, we have sequenced the genomes of species infecting macaques, rabbits, dogs and rats and compared them to available genomes of species infecting humans, mice and rats. Complete whole genome sequence data enables analysis and robust phylogeny, identification of important genetic features of the host adaptation, and estimation of speciation timing relative to the rise of their mammalian hosts. Our data reveals insights into the evolution of P. jirovecii, the sole member of the genus able to infect humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

