Can reasoned mass testing impact covid-19 outcomes in wide community contexts? An evidence-based opinion
- PMID: 33686907
- PMCID: PMC8079040
- DOI: 10.1080/20477724.2021.1878444
Can reasoned mass testing impact covid-19 outcomes in wide community contexts? An evidence-based opinion
Abstract
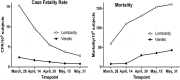
We describe the early phases of a COVID-19 epidemic in two contiguous Italian regions, Lombardy and Veneto, which were heavily and simultaneously hit by SARS-CoV-2 in Italy but showed markedly different disease outcome in terms of case fatality rate, SARS-CoV-2-attributable mortality and hospitalization. We discuss data limitations together with similarities and differences of the regional context possibly affecting COVID-19 control in the two regions. We conclude that the better COVID-19 outcome in Veneto was due, at least in part, to the adoption of a strategy of active search of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections (Reasoned Mass Testing), instead of a strategy strictly based on the detection of symptomatic cases.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 Mass testing; case Fatality Rate; covid-19; lombardy; mortality; veneto.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Comment on
-
Real estimates of mortality following COVID-19 infection.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Jul;20(7):773. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30195-X. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32171390 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of lockdown on Covid-19 case fatality rate and viral mutations spread in 7 countries in Europe and North America.J Transl Med. 2020 Sep 2;18(1):338. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02501-x. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32878627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crisanti A, Cassone A. In one Italian town, we showed mass testing could eradicate the coronavirus.TheGuardian https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2020/mar/20/eradicated-coronav....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous