Peripheral ischemic limb necrosis (Acro-ischemia) associated with severe COVID-19 patients (COVID-19 limbs): A report of three cases
- PMID: 33686981
- PMCID: PMC8104337
- DOI: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_470_20
Peripheral ischemic limb necrosis (Acro-ischemia) associated with severe COVID-19 patients (COVID-19 limbs): A report of three cases
Abstract
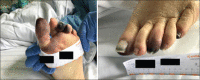
The association between severe coronavirus disease 2019 and hypercoagulable state was observed in many reports. This may be explained by the presence of hypoxia, severe systemic inflammatory response, immobilization due to intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and diffuse intravascular coagulation. We report three patients who were admitted to our respiratory ICU with acute severe respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) requiring mechanical ventilation due severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection, who developed severe limb ischemia during the course of the disease.
Keywords: ARDS; D-dimer; coronavirus disease 2019; limb ischemia; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


References
-
- WHO Director-General's Remarks at the Media Briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February. 2020. [Last accessed on 2020 May 04]. Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at... .
-
- Fan BE, Chong VCL, Chan SSW, Lim GH, Lim KGE, Tan GB, et al. Hematologic parameters in patients with COVID-19 infection. Am J Hematol. 2020;95:E131–4. - PubMed
-
- The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41:145–51. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

