The Role of Replication Clamp-Loader Protein HolC of Escherichia coli in Overcoming Replication/Transcription Conflicts
- PMID: 33688004
- PMCID: PMC8092217
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00184-21
The Role of Replication Clamp-Loader Protein HolC of Escherichia coli in Overcoming Replication/Transcription Conflicts
Abstract
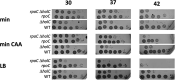
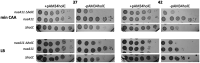
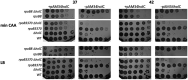
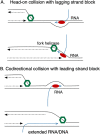
In Escherichia coli, DNA replication is catalyzed by an assembly of proteins, the DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. This complex includes the polymerase and proofreading subunits, the processivity clamp, and clamp loader complex. The holC gene encodes an accessory protein (known as χ) to the core clamp loader complex and is the only protein of the holoenzyme that binds to single-strand DNA binding protein, SSB. HolC is not essential for viability, although mutants show growth impairment, genetic instability, and sensitivity to DNA damaging agents. In this study, we isolate spontaneous suppressor mutants in a ΔholC strain and identify these by whole-genome sequencing. Some suppressors are alleles of RNA polymerase, suggesting that transcription is problematic for holC mutant strains, or alleles of sspA, encoding stringent starvation protein. Using a conditional holC plasmid, we examine factors affecting transcription elongation and termination for synergistic or suppressive effects on holC mutant phenotypes. Alleles of RpoA (α), RpoB (β), and RpoC (β') RNA polymerase holoenzyme can partially suppress loss of HolC. In contrast, mutations in transcription factors DksA and NusA enhanced the inviability of holC mutants. HolC mutants showed enhanced sensitivity to bicyclomycin, a specific inhibitor of Rho-dependent termination. Bicyclomycin also reverses suppression of holC by rpoA, rpoC, and sspA An inversion of the highly expressed rrnA operon exacerbates the growth defects of holC mutants. We propose that transcription complexes block replication in holC mutants and that Rho-dependent transcriptional termination and DksA function are particularly important to sustain viability and chromosome integrity.IMPORTANCE Transcription elongation complexes present an impediment to DNA replication. We provide evidence that one component of the replication clamp loader complex, HolC, of Escherichia coli is required to overcome these blocks. This genetic study of transcription factor effects on holC growth defects implicates Rho-dependent transcriptional termination and DksA function as critical. It also implicates, for the first time, a role of SspA, stringent starvation protein, in avoidance or tolerance of replication/replication conflicts. We speculate that HolC helps avoid or resolve collisions between replication and transcription complexes, which become toxic in HolC's absence.
Keywords: DNA repair; DNA replication; stringent response; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2021 Cooper et al.
Figures
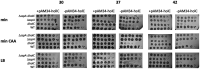
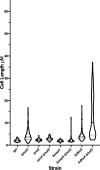
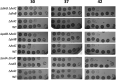
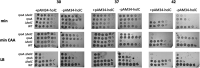



Comment in
-
DNA polymerase III protein, HolC, helps resolve replication/transcription conflicts.Microb Cell. 2021 May 6;8(6):143-145. doi: 10.15698/mic2021.06.753. Microb Cell. 2021. PMID: 34055967 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
DNA polymerase III protein, HolC, helps resolve replication/transcription conflicts.Microb Cell. 2021 May 6;8(6):143-145. doi: 10.15698/mic2021.06.753. Microb Cell. 2021. PMID: 34055967 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative complexes formed by the Escherichia coli clamp loader accessory protein HolC (x) with replication protein HolD (ψ) and repair protein YoaA.DNA Repair (Amst). 2021 Apr;100:103006. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.103006. Epub 2021 Feb 2. DNA Repair (Amst). 2021. PMID: 33582602 Free PMC article.
-
ssb gene duplication restores the viability of ΔholC and ΔholD Escherichia coli mutants.PLoS Genet. 2014 Oct 16;10(10):e1004719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004719. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25329071 Free PMC article.
-
DksA and DNA double-strand break repair.Curr Genet. 2019 Dec;65(6):1297-1300. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00983-x. Epub 2019 May 10. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 31076845 Review.
-
The enigmatic role of Mfd in replication-transcription conflicts in bacteria.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Sep;81:102659. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102659. Epub 2019 Jul 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31311770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Analysis of DinG Family Helicase YoaA and Its Interaction with Replication Clamp Loader Protein HolC in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2021 Aug 20;203(18):e0022821. doi: 10.1128/JB.00228-21. Epub 2021 Aug 20. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34181484 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a Defective Clamp Loader Complex of DNA Polymerase III on Growth and SOS Response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microorganisms. 2022 Feb 12;10(2):423. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020423. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208877 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA damage response of Escherichia coli, revisited: Differential gene expression after replication inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 2;121(27):e2407832121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2407832121. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38935560 Free PMC article.
-
A mobile CRISPRi collection enables genetic interaction studies for the essential genes of Escherichia coli.Cell Rep Methods. 2024 Jan 22;4(1):100693. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100693. Cell Rep Methods. 2024. PMID: 38262349 Free PMC article.
-
AamA-mediated epigenetic control of genome-wide gene expression and phenotypic traits in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978.Microb Genom. 2023 Aug;9(8):mgen001093. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001093. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 37589545 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

