A safe and highly efficacious measles virus-based vaccine expressing SARS-CoV-2 stabilized prefusion spike
- PMID: 33688034
- PMCID: PMC8000430
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2026153118
A safe and highly efficacious measles virus-based vaccine expressing SARS-CoV-2 stabilized prefusion spike
Abstract
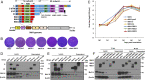
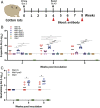
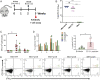
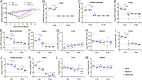
The current pandemic of COVID-19 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) highlights an urgent need to develop a safe, efficacious, and durable vaccine. Using a measles virus (rMeV) vaccine strain as the backbone, we developed a series of recombinant attenuated vaccine candidates expressing various forms of the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein and its receptor binding domain (RBD) and evaluated their efficacy in cotton rat, IFNAR-/-mice, IFNAR-/--hCD46 mice, and golden Syrian hamsters. We found that rMeV expressing stabilized prefusion S protein (rMeV-preS) was more potent in inducing SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibodies than rMeV expressing full-length S protein (rMeV-S), while the rMeVs expressing different lengths of RBD (rMeV-RBD) were the least potent. Animals immunized with rMeV-preS produced higher levels of neutralizing antibody than found in convalescent sera from COVID-19 patients and a strong Th1-biased T cell response. The rMeV-preS also provided complete protection of hamsters from challenge with SARS-CoV-2, preventing replication in lungs and nasal turbinates, body weight loss, cytokine storm, and lung pathology. These data demonstrate that rMeV-preS is a safe and highly efficacious vaccine candidate, supporting its further development as a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 vaccine; measles virus vector; prefusion spike.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: The Ohio State University has filed an invention report for the measles virus-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine platform.
Figures




References
-
- Thanh Le T., et al., The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 19, 305–306 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI142256/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI090060/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123661/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL154001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI090060/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150473/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI137567/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130110/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI112381/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 HG008935/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI142733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA260582/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI146690/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI093848/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI151175/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI151230/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI42733/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI101175/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI112524/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

