Evaluation of Beneficial and Adverse Effects of a Diet Supplemented with Schisandrae Fructus Seed Ethanol Extract on Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in Normal and Hypercholesterolemic/Hyperglycemic Mice
- PMID: 33688367
- PMCID: PMC7920717
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8858962
Evaluation of Beneficial and Adverse Effects of a Diet Supplemented with Schisandrae Fructus Seed Ethanol Extract on Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in Normal and Hypercholesterolemic/Hyperglycemic Mice
Abstract
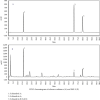
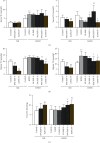
Schisandrae Fructus (SF), the fruit of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baillon, has been used for the treatment of liver injury and metabolism-related disorders in China. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of supplementation with ethanol extract of SF seed (EtSF-S) on serum/hepatic lipid and glucose levels as well as fecal total cholesterol (TC) contents in mice fed a normal diet (ND) or high-fat/fructose diet (HFFD) containing 15% lard oil and 15% fructose. Female ICR mice (18-20 g in body weight) were fed with ND or HFFD for 3 months, and then EtSF-S was added to both chow diets at increasing concentrations of 1, 5, and 10% (w/w). Thirty days later, serum and hepatic lipids, including TC, triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and glucose, were measured. Dietary supplementation with EtSF-S reduced hepatic TC (36 and 18%) and TG levels (38 and 28%) and increased serum HDL/LDL ratio (16 and 26%) in both ND- and HFFD-fed mice, respectively. Moreover, supplementation with EtSF-S elevated serum HDL (31%) in HFFD-fed mice and reduced serum LDL (27%) in ND-fed mice. EtSF-S treatment reduced fat mass (40%) in ND-fed mice and increased fecal TC contents (33%) in HFFD-fed mice. EtSF-S supplementation decreased hepatic glucose contents (29%) in both ND- and HFFD-fed mice. However, diet supplemented with EtSF-S elevated serum TG levels (up to 123%) and hepatic size (28%), but more importantly, suppressed the body weight gain (approximately 130%) in mice fed with HFFD. These findings suggested that dietary supplementation with EtSF-S as natural herbal function food may be a useful strategy for the treatment of patients with fatty liver disease or overweight without a high intake of sugar and fat.
Copyright © 2021 Xiao-Yan Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lowndes J., Sinnett S., Yu Z., Rippe J. The effects of fructose-containing sugars on weight, body composition and cardiometabolic risk factors when consumed at up to the 90th percentile population consumption level for fructose. Nutrients. 2014;6(8):3153–3168. doi: 10.3390/nu6083153. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schwab U., Lauritzen L., Tholstrup T., et al. Effect of the amount and type of dietary fat on cardiometabolic risk factors and risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer: a systematic review. Food & Nutrition Research. 2014;58(1) doi: 10.3402/fnr.v58.25145.25145 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Z. L., Xie L. Z., Zhu J., Li G. Q., Grant S. J., Liu J. P. Herbal medicines for fatty liver diseases. Cochrane. Database Systematic Reviews. 2013;8CD009059 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

