Adapting to the COVID-19 Pandemic at a Quaternary Care Hospital in the Middle East Gulf Region
- PMID: 33688399
- PMCID: PMC7898996
- DOI: 10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_168_20
Adapting to the COVID-19 Pandemic at a Quaternary Care Hospital in the Middle East Gulf Region
Figures

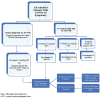



References
-
- Worldometers. info About Worldometer COVID-19 data-Worldometer. 2020. [[Last accessed on 28 Jun 2020]]. Available from: https://wwwworldometersinfo/coronavirus/about/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
