Transfer of Th17 from Adult Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats Accelerates Development of Hypertension in Juvenile Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 33688497
- PMCID: PMC7914094
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6633825
Transfer of Th17 from Adult Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats Accelerates Development of Hypertension in Juvenile Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
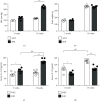
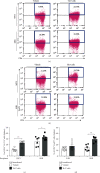
Hypertension develops in the recipient rats that are transferred with the activated T helper (Th) 17 cells of the donor rats exposed to high-fructose or high-salt intake. This result suggests that a pathologic Th17 cell plays a role in the development and maintenance of hypertension. Here, we tested the hypothesis that the transfer of Th17 cells from adult spontaneous hypertensive rats (SHR) accelerates the development of hypertension in juvenile SHR. The tail-cuff method was used to measure systolic blood pressure. T cell (Th17 and regulatory T (Treg)) profiling was analyzed by flow cytometry. The expressions of Th17-related interleukin- (IL-) 17A and Treg-related IL-10 were measured by ELISA. Th17 cells isolated from adult SHR were intraperitoneally injected into juvenile recipient SHR and Wistar-Kyoto rats (WKY). SHR exhibited prominent development of hypertension at 15 weeks. The proportion of CD4+IL-17A+ (Th17) cells among Th cells increased whereas the proportion of CD4+FoxP3+ (Treg) cells decreased in SHR, as compared to WKY. The serum levels of IL-17A increased gradually with aging in SHR, but the serum levels of IL-10 did not. The serum levels of IL-17A and IL-10 seemed to be well related to the proportion of Th17 cells and Treg cells, respectively. Injection of Th17 cells isolated from adult SHR accelerates the development of hypertension in juvenile SHR but not in juvenile WKY though it increased the proportion of Th17 cells in juvenile recipient WKY and SHR. The transfer of Th17 cells from adult SHR accelerates the development of hypertension in juvenile SHR. These results implicate that the hypertension in SHR is ascribed to activation of Th17 cells.
Copyright © 2021 Jee Young Kim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activated pathogenic Th17 lymphocytes induce hypertension following high-fructose intake in Dahl salt-sensitive but not Dahl salt-resistant rats.Dis Model Mech. 2020 May 27;13(5):dmm044107. doi: 10.1242/dmm.044107. Dis Model Mech. 2020. PMID: 32179549 Free PMC article.
-
Female spontaneously hypertensive rats have a compensatory increase in renal regulatory T cells in response to elevations in blood pressure.Hypertension. 2014 Sep;64(3):557-64. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03512. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 24914200 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal CD161+ immune cells and retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor γt-mediate enhanced IL-17F expression in the setting of genetic hypertension.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Sep;140(3):809-821.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.11.039. Epub 2017 Jan 16. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28093217 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in T cells in hypertension.Clin Ther. 2014 Dec 1;36(12):1882-1900. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.07.011. Epub 2014 Aug 16. Clin Ther. 2014. PMID: 25134971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin 17A: Key Player in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension and a Potential Therapeutic Target.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021 Mar 5;23(3):13. doi: 10.1007/s11906-021-01128-7. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021. PMID: 33666761 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PVAT-conditioned media from Dahl S rats on high fat diet promotes inflammatory cytokine secretion by activated T cells prior to the development of hypertension.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 3;19(10):e0302503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302503. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39361560 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Pressure Variability and Low-Grade Inflammation in Pediatric Patients with Primary Hypertension.J Clin Med. 2025 Aug 13;14(16):5737. doi: 10.3390/jcm14165737. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40869561 Free PMC article.
-
Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in hypertension.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024 Jun;21(6):396-416. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00964-1. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38172242 Review.
-
O-Linked β-N-Acetylglucosamine Modification: Linking Hypertension and the Immune System.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 17;13:852115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.852115. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35371030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myristolated Serotonin 2A Receptor Peptide Promotes Long-Lasting Blood Pressure-Lowering and Reno protection in Hypertensive Rat Species.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J. 2022 Dec;6(3):10.31038/EDMJ.2022631. doi: 10.31038/EDMJ.2022631. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab J. 2022. PMID: 36919081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saleh M. A., Norlander A. E., Madhur M. S. Inhibition of interleukin-17A, but not interleukin-17F, signaling lowers blood pressure, and reduces end-organ inflammation in angiotensin II–induced hypertension. JACC: Basic to Translational Science. 2016;1(7):606–616. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2016.07.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

