This is a preprint.
IL-13 is a driver of COVID-19 severity
- PMID: 33688686
- PMCID: PMC7941663
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.06.18.20134353
IL-13 is a driver of COVID-19 severity
Update in
-
IL-13 is a driver of COVID-19 severity.JCI Insight. 2021 Aug 9;6(15):e150107. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.150107. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34185704 Free PMC article.
Abstract
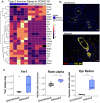
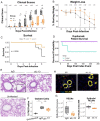
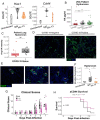
Immune dysregulation is characteristic of the more severe stages of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Understanding the mechanisms by which the immune system contributes to COVID-19 severity may open new avenues to treatment. Here we report that elevated interleukin-13 (IL-13) was associated with the need for mechanical ventilation in two independent patient cohorts. In addition, patients who acquired COVID-19 while prescribed Dupilumab had less severe disease. In SARS-CoV-2 infected mice, IL-13 neutralization reduced death and disease severity without affecting viral load, demonstrating an immunopathogenic role for this cytokine. Following anti-IL-13 treatment in infected mice, in the lung, hyaluronan synthase 1 (Has1) was the most downregulated gene and hyaluronan accumulation was decreased. Blockade of the hyaluronan receptor, CD44, reduced mortality in infected mice, supporting the importance of hyaluronan as a pathogenic mediator, and indicating a new role for IL-13 in lung disease. Understanding the role of IL-13 and hyaluronan has important implications for therapy of COVID-19 and potentially other pulmonary diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: William A. Petri, Jr. receives research funding from Regeneron, Inc. which is the maker of Dupilumab. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Babraham Bioinformatics - FastQC A Quality Control tool for High Throughput Sequence Data.
-
- Bell T.J., Brand O.J., Morgan D.J., Salek-Ardakani S., Jagger C., Fujimori T., Cholewa L., Tilakaratna V., Östling J., Thomas M., Day A.J., Snelgrove R.J., and Hussell T.. 2019. Defective lung function following influenza virus is due to prolonged, reversible hyaluronan synthesis. Matrix Biol. 80:14–28. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2018.06.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borthwick L.A., Barron L., Hart K.M., Vannella K.M., Thompson R.W., Oland S., Cheever A., Sciurba J., Ramalingam T.R., Fisher A.J., and Wynn T.A.. 2016. Macrophages are critical to the maintenance of IL-13-dependent lung inflammation and fibrosis. Mucosal Immunol. 9:38–55. doi:10.1038/mi.2015.34. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cantuti-Castelvetri L., Ojha R., Pedro L.D., Djannatian M., Franz J., Kuivanen S., van der Meer F., Kallio K., Kaya T., Anastasina M., Smura T., Levanov L., Szirovicza L., Tobi A., Kallio-Kokko H., Österlund P., Joensuu M., Meunier F.A., Butcher S.J., Winkler M.S., Mollenhauer B., Helenius A., Gokce O., Teesalu T., Hepojoki J., Vapalahti O., Stadelmann C., Balistreri G., and Simons M.. 2020. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science. 370:856–860. doi:10.1126/science.abd2985. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
