Advances in the automated synthesis of 6-[18F]Fluoro-L-DOPA
- PMID: 33689056
- PMCID: PMC7947162
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-021-00126-z
Advances in the automated synthesis of 6-[18F]Fluoro-L-DOPA
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Advances in the automated synthesis of 6-[18F]Fluoro-L-DOPA.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2021 May 20;6(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s41181-021-00132-1. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2021. PMID: 34018059 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
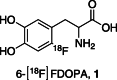
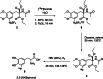
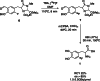
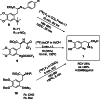
The neurotracer 6-[18F] FDOPA has been, for many years, a powerful tool in PET imaging of neuropsychiatric diseases, movement disorders and brain malignancies. More recently, it also demonstrated good results in the diagnosis of other malignancies such as neuroendocrine tumours, pheochromocytoma or pancreatic adenocarcinoma.The multiple clinical applications of this tracer fostered a very strong interest in the development of new and improved methods for its radiosynthesis. The no-carrier-added nucleophilic 18F-fluorination process has gained increasing attention, in recent years, due to the high molar activities obtained, when compared with the other methods although the radiochemical yield remains low (17-30%). This led to the development of several nucleophilic synthetic processes in order to obtain the product with molar activity, radiochemical yield and enantiomeric purity suitable for human PET studies.Automation of the synthetic processes is crucial for routine clinical use and compliance with GMP requirements. Nevertheless, the complexity of the synthesis makes the production challenging, increasing the chance of failure in routine production. Thus, for large-scale clinical application and wider use of this radiopharmaceutical, progress in the automation of this complex radiosynthesis is of critical importance.This review summarizes the most recent developments of 6-[18F]FDOPA radiosynthesis and discusses the key issues regarding its automation for routine clinical use.
Keywords: 6-[18F]FDOPA; Automated synthesis; Nonproteinogenic amino acid; PET; Radiochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship or publication of this article.
Figures
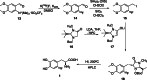
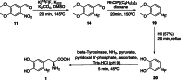





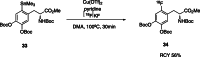



References
-
- Adam MJ, Jivan S. Synthesis and purification of l-6-[18F]fluorodopa. Int J Radiat Appl Instrumentation Part A Appl Radiat Isot. 1988;39(12):1203–1206.
-
- Adam MJ, Ruth TJ, Grierson JR, Abeysekera B, Pate BD. Routine Synthesis of L- [18F] 6-Fluorodopa with Fluorine- 18 Acetyl Hypofluorite. J Nucl Med. 1986;27:1462–1466. - PubMed
-
- Bishop A, Satyamurthy N, Bida G, Barrio JR. Chemical reactivity of the 18F electrophilic reagents from the 18O(p,n)18F gas target systems. Nucl Med Biol. 1996;23(5):559–565. - PubMed
-
- Bose SK, Turkheimer FE, Howes OD, Mehta MA, Cunliffe R, Stokes PR, et al. Classification of schizophrenic patients and healthy controls using [18F] fluorodopa PET imaging. Schizophr Res. 2008;106(2–3):148–155. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
