A synthetic small molecule stalls pre-mRNA splicing by promoting an early-stage U2AF2-RNA complex
- PMID: 33689684
- PMCID: PMC8380659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.02.007
A synthetic small molecule stalls pre-mRNA splicing by promoting an early-stage U2AF2-RNA complex
Abstract
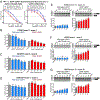
Dysregulated pre-mRNA splicing is an emerging Achilles heel of cancers and myelodysplasias. To expand the currently limited portfolio of small-molecule drug leads, we screened for chemical modulators of the U2AF complex, which nucleates spliceosome assembly and is mutated in myelodysplasias. A hit compound specifically enhances RNA binding by a U2AF2 subunit. Remarkably, the compound inhibits splicing of representative substrates and stalls spliceosome assembly at the stage of U2AF function. Computational docking, together with structure-guided mutagenesis, indicates that the compound bridges the tandem U2AF2 RNA recognition motifs via hydrophobic and electrostatic moieties. Cells expressing a cancer-associated U2AF1 mutant are preferentially killed by treatment with the compound. Altogether, our results highlight the potential of trapping early spliceosome assembly as an effective pharmacological means to manipulate pre-mRNA splicing. By extension, we suggest that stabilizing assembly intermediates may offer a useful approach for small-molecule inhibition of macromolecular machines.
Keywords: S34F mutant; U2AF(35); U2AF(65); U2AF1; myelodysplastic syndrome; ribonucleoprotein targeting; spliceosome inhibition; splicing factor mutation; therapeutic strategy.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

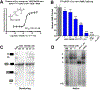
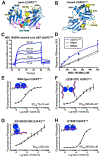
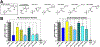
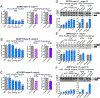
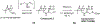
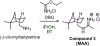
Comment in
-
Stuck on UUUU: New splicing inhibitors enhance U2AF2-RNA binding.Cell Chem Biol. 2021 Aug 19;28(8):1106-1108. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.07.021. Cell Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34416141
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

