Development and application of novel immunoassays for eosinophil granule major basic proteins to evaluate eosinophilia and myeloproliferative disorders
- PMID: 33689807
- PMCID: PMC8107142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2021.113015
Development and application of novel immunoassays for eosinophil granule major basic proteins to evaluate eosinophilia and myeloproliferative disorders
Abstract
Background: During eosinophil differentiation, the granule eosinophil major basic protein 1 (eMBP1) is synthesized as a 32-kDa precursor form, referred to as proMBP1, which is processed into the 14-kDa mature form of eMBP1. The prevalence of these two forms of MBP1 in most pathological conditions remains unknown.
Objective: To develop the immunoassays that differentiate mature eMBP1 and proMBP1 and apply them to analyze their levels in biological fluids from patients with eosinophilia and hematologic disorders.
Methods: We produced a series of monoclonal antibodies and selected pairs capable of discriminating between the two molecular forms of eMBP1. Radioimmunoassay (RIA) was performed to simultaneously quantitate the levels of mature eMBP1 and proMBP1 in secretions from patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) and sera from patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and other myeloproliferative disorders.
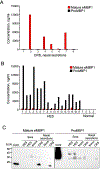
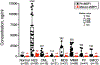
Results: The novel immunoassays possessed less than 1% crossreactivity between mature eMBP1 and proMBP1. Mature eMBP1, but not proMBP1, was found in nasal secretions of CRS patients. In contrast, elevated serum levels of mature eMBP1 and proMBP1 were observed in approximately 60% and 90% of HES patients, respectively, with proMBP1 present in greater quantities than mature eMBP1. Patients with several myeloproliferative disorders also showed high serum levels of proMBP1 while mature eMBP1 remained at basal levels.
Conclusion: The novel immunoassays successfully differentiated mature eMBP1 and proMBP1 in human biological fluids. Further studies addressing the clinical correlates of these assays will help to develop biomarkers to diagnose and monitor patients with eosinophilia and myeloproliferative disorders.
Keywords: Eosinophilia; Eosinophils; MBP; Myeloproliferative disorders; proMBP.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors do not have any conflicts related to this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Major basic protein homolog (MBP2): a specific human eosinophil marker.J Immunol. 2006 Nov 15;177(10):7340-5. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.7340. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17082653
-
Eosinophil granule major basic protein 1 deposition in eosinophilic esophagitis correlates with symptoms independent of eosinophil counts.Dis Esophagus. 2019 Dec 30;32(11):doz055. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz055. Dis Esophagus. 2019. PMID: 31310661
-
Clinical correlates of serum pro-major basic protein in a spectrum of eosinophilic disorders and myelofibrosis.Acta Haematol. 2008;120(3):158-64. doi: 10.1159/000178148. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Acta Haematol. 2008. PMID: 19039208
-
World Health Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2014 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management.Am J Hematol. 2014 Mar;89(3):325-37. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23664. Am J Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24577808 Review.
-
Practical Approach to Children Presenting with Eosinophila and Hypereosinophilia.Curr Pediatr Rev. 2020;16(2):81-88. doi: 10.2174/1573396315666191114150438. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2020. PMID: 31729944 Review.
Cited by
-
Urine eosinophil-derived neurotoxin: A potential marker of activity in select eosinophilic disorders.Allergy. 2023 Jan;78(1):258-269. doi: 10.1111/all.15481. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Allergy. 2023. PMID: 35971862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Plager DA, Adolphson CR, Gleich GJ. A novel human homolog of eosinophil major basic protein. Immunol Rev. 2001;179:192–202. - PubMed
-
- Gleich GJ, Adolphson CR. The eosinophilic leukocyte: structure and function. Adv Immunol. 1986;39:177–253. - PubMed
-
- Gleich GJ. Samter’s Immunologic Disease 1979. p. 204–45.
-
- Gleich GJ, Frigas E, Loegering DA, Wassom DL, Steinmuller D. Cytotoxic properties of the eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979;123(6):2925–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

