Gene alteration in zebrafish exposed to a mixture of substances of abuse
- PMID: 33689951
- PMCID: PMC8053679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116777
Gene alteration in zebrafish exposed to a mixture of substances of abuse
Abstract
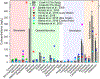
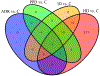
A recent surge in the use and abuse of diverse prescribed psychotic and illicit drugs necessitates the surveillance of drug residues in source water and the associated ecological impacts of chronic exposure to the aquatic organism. Thirty-six psychotic and illicit drug residues were determined in discharged wastewater from two centralized municipal wastewater treatment facilities and two wastewater receiving creeks for seven consecutive days in Kentucky. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae were exposed to the environmental relevant mixtures of all drug residues, all illicit drugs, and all prescribed psychotic drugs. The extracted RNA from fish homogenates was sequenced, and differentially expressed sequences were analyzed for known or predicted nervous system expression, and screened annotated protein-coding genes to the true environmental cocktail mixture. Illicit stimulant (cocaine and one metabolite), opioids (methadone, methadone metabolite, and oxycodone), hallucinogen (MDA), benzodiazepine (oxazepam and temazepam), carbamazepine, and all target selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors including sertraline, fluoxetine, venlafaxine, and citalopram were quantified in 100% of collected samples from both creeks. The high dose cocktail mixture exposure group revealed the largest group of differentially expressed genes: 100 upregulated and 77 downregulated (p ≤ 0.05; q ≤ 0.05). The top 20 differentially expressed sequences in each exposure group comprise 82 unique transcripts corresponding to 74% annotated genes, 7% non-coding sequences, and 19% uncharacterized sequences. Among 61 differentially expressed sequences that corresponded to annotated protein-coding genes, 23 (38%) genes or their homologs are known to be expressed in the nervous system of fish or other organisms. Several of the differentially expressed sequences are associated primarily with the immune system, including several major histocompatibility complex class I and interferon-induced proteins. Interleukin-1 beta (downregulated in this study) abnormalities are considered a risk factor for psychosis. This is the first study to assess the contributions of multiple classes of psychotic and illicit drugs in combination with developmental gene expression.
Keywords: Illicit drugs; Nervous system; Next generation gene sequencing; Psychotic drugs; RNA-Seq; Zebrafish.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
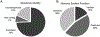
Similar articles
-
Global gene expression in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (fluoxetine and sertraline) reveals unique expression profiles and potential biomarkers of exposure.Environ Pollut. 2012 Aug;167:163-70. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.03.039. Epub 2012 May 9. Environ Pollut. 2012. PMID: 22575097
-
Transcriptome networks and physiology related to cardiac function and motor activity are perturbed in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) following exposure to the antidepressant citalopram.Environ Pollut. 2024 Nov 15;361:124767. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.124767. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Environ Pollut. 2024. PMID: 39168440
-
Global transcriptomic analysis of zebrafish in response to embryonic exposure to three antidepressants, amitriptyline, fluoxetine and mianserin.Aquat Toxicol. 2017 Nov;192:274-283. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.09.027. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Aquat Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28992598
-
Effects of waterborne antidepressants on non-target animals living in the aquatic environment: A review.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Aug 1;631-632:789-794. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.076. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 29727988 Review.
-
Aquatic ecotoxicology of fluoxetine.Toxicol Lett. 2003 May 15;142(3):169-83. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4274(03)00066-3. Toxicol Lett. 2003. PMID: 12691711 Review.
Cited by
-
Could Alcohol Abuse and Dependence on Junk Foods Inducing Obesity and/or Illicit Drug Use Represent Danger to Liver in Young People with Altered Psychological/Relational Spheres or Emotional Problems?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10406. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810406. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The new psychoactive substances 25H-NBOMe and 25H-NBOH induce abnormal development in the zebrafish embryo and interact in the DNA major groove.Curr Res Toxicol. 2021 Nov 22;2:386-398. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2021.11.002. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34888530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson JF, Siller E, Barral JM, 2011. The neurodegenerative-disease-related protein sacsin is a molecular chaperone. J. Mol. Biol 411, 870–880. - PubMed
-
- Appelbaum L, Skariah G, Mourrain P, Mignot E, 2007. Comparative expression of p2x receptors and ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3 in hypocretin and sensory neurons in zebrafish. Brain Res. 1174, 66–75. - PubMed
-
- Baker DR; Barron L; Kasprzyk-Hordern B, 2014. Illicit and pharmaceutical drug consumption estimated via wastewater analysis. Part A: chemical analysis and drug use estimates. Sci. Total Environ 487, 629–641. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

