Follow-up testing of borderline SARS-CoV-2 patients by rRT-PCR allows early diagnosis of COVID-19
- PMID: 33689985
- PMCID: PMC7891066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115350
Follow-up testing of borderline SARS-CoV-2 patients by rRT-PCR allows early diagnosis of COVID-19
Abstract
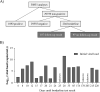
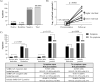
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in nasopharyngeal samples using the real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) is the gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19. Determination of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by rRT-PCR sometimes results in an inconclusive test result due to a high cycle threshold-value. We retrospectively analyzed 30,851 SARS-CoV-2 rRT-PCR test results. Borderline positivity was considered as the presence of ≤25 viral copies per milliliter, while no amplification was considered as a negative test result. Of all test results, 204 were answered as borderline, of which 107 were accompanied by a follow-up test within 96 hours. Of the 107 follow-up samples, 10 (9.35%) were found positive for SARS-CoV-2. COVID-19 symptoms were not predictive for testing positive in the follow-up test. The positive SARS-CoV-2 samples in the follow-up group represented 0.92% of all positive test results, highlighting the need for retesting and increased hygienic measures for borderline SARS-CoV-2 patients [NCT04636294].
Keywords: Borderline; COVID-19; Molecular diagnostics; SARS-CoV-2; rRT-PCR.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Botta M, Tsonas AM, Pillay J, Boers LS, Algera AG, Bos LDJ, et al. Ventilation management and clinical outcomes in invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PRoVENT-COVID): a national, multicentre, observational cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;19:1–10. doi: 10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30459-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

