Fluoxetine as an anti-inflammatory therapy in SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 33691249
- PMCID: PMC7904450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111437
Fluoxetine as an anti-inflammatory therapy in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
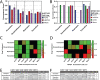
Hyperinflammatory response caused by infections such as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) increases organ failure, intensive care unit admission, and mortality. Cytokine storm in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) drives this pattern of poor clinical outcomes and is dependent upon the activity of the transcription factor complex nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kappaB) and its downstream target gene interleukin 6 (IL6) which interacts with IL6 receptor (IL6R) and the IL6 signal transduction protein (IL6ST or gp130) to regulate intracellular inflammatory pathways. In this study, we compare transcriptomic signatures from a variety of drug-treated or genetically suppressed (i.e. knockdown) cell lines in order to identify a mechanism by which antidepressants such as fluoxetine demonstrate non-serotonergic, anti-inflammatory effects. Our results demonstrate a critical role for IL6ST and NF-kappaB Subunit 1 (NFKB1) in fluoxetine's ability to act as a potential therapy for hyperinflammatory states such as asthma, sepsis, and COVID-19.
Keywords: Antidepressants; COVID-19; Coronavirus disease 2019; Cytokine IL6; Cytokine storm; Fluoxetine; Inflammation; Nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1; SARS-CoV-2; SSRIs; Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; Sepsis; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Transcription factor NF-κB.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Tanaka T., Narazaki M., Kishimoto T. Immunotherapeutic implications of IL-6 blockade for cytokine storm. Immunotherapy. 2016;8(8):959–970. - PubMed
-
- Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wu W., Xie X., Yin W., Li H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

