Update on Morbidity and Mortality in Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease
- PMID: 33693057
- PMCID: PMC7943067
- DOI: 10.1177/2397198320915042
Update on Morbidity and Mortality in Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
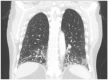
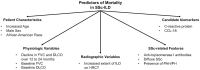
Contemporary studies of systemic sclerosis (SSc) consistently demonstrate that interstitial lung (ILD) is a leading cause of disease-related death. This review summarizes morbidity and mortality outcomes in SSc-ILD patients from high-quality observational and interventional studies over the last 50 years. The data presented suggest a trend for improved morbidity and mortality outcomes among present day SSc-ILD patients. Specifically, SSc-ILD patients appear to be living longer from the time of the initial diagnosis. Despite improved survival, the number one cause of death for most SSc-ILD patients remains respiratory failure from ILD. This review describes the most important demographic, clinical, and biological factors, which affect mortality in SSc-ILD, and could be used to help stratify patients for closer monitoring and more aggressive initial treatment. The review concludes with an overview of future research needed to (1) understand how to personalize the care of SSc-ILD patients to improve morbidity and mortality outcomes; and (2) investigate whether novel therapeutic interventions (e.g., anti-fibrotics, hematopoetic stem-cell transplantation) offer any meaningful long-term survival advantage over the current standard of care.
Keywords: immunosuppression; interstitial lung disease; mortality; scleroderma; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69(10): 1809–1815. - PubMed
-
- Rubio-Rivas M, Royo C, Simeón CP, et al. Mortality and survival in systemic sclerosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2014; 44(2): 208–219. - PubMed
-
- D’Angelo WA, Fries JF, Masi AT, et al. Pathologic observations in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). A study of fifty-eight autopsy cases and fifty-eight matched controls. Am J Med 1969; 46(3): 428–440. - PubMed
-
- Weaver AL, Divertie MB, Titus JL. Pulmonary scleroderma. Dis Chest 1968; 54: 490–498. - PubMed
