Prognostic Importance of Multiple Nutrition Screening Indexes for 1-Year Mortality in Hospitalized Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Patients
- PMID: 33693118
- PMCID: PMC7890280
- DOI: 10.1253/circrep.CR-18-0018
Prognostic Importance of Multiple Nutrition Screening Indexes for 1-Year Mortality in Hospitalized Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Patients
Abstract
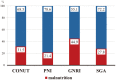
Background: The purpose of the study was to evaluate the impact of nutritional status on 1-year mortality in hospitalized patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). Methods and Results: We enrolled 457 hospitalized ADHF patients. Previously established objective nutritional indexes (controlling nutritional status [CONUT], prognostic nutritional index [PNI], geriatric nutritional risk index [GNRI], and subjective global assessment [SGA]) were evaluated at hospital admission. Malnutrition was defined as CONUT score ≥5, PNI score <38, GNRI score <92, and SGA scores B and C. The frequencies of malnutrition based on CONUT, PNI, GNRI, and SGA were 31.5%, 21.4%, 44.9%, and 27.8%, respectively. All indexes were related to the occurrence of 1-year mortality on univariate Cox regression analysis (P<0.05). We constructed a reference model using age, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, sodium concentration, and renal function on multivariable Cox regression analysis. Adding SGA to the reference model significantly improved both net reclassification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (0.344, P=0.002; 0.012, P=0.049; respectively). Other indexes (CONUT, PNI, and GNRI scores) significantly improved NRI (0.254, P=0.019; 0.273, P=0.013; 0.306, P=0.006; respectively). Conclusions: Nutritional screening assessed at hospital admission was appropriate for the prediction of 1-year mortality in hospitalized patients with ADHF.
Keywords: Acute heart failure; Nutrition assessment; Prognosis.
Copyright © 2019, THE JAPANESE CIRCULATION SOCIETY.
Conflict of interest statement
H.I. received lecture fees from Astellas Pharma, Bayer Pharmaceutical, Daiichi-Sankyo Pharms, and MSD. T.M. received lecture fees from Bayer Pharmaceutical, Daiichi-Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Kowa, MSD, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharma, Pfizer Japan, Sanofi-aventis, and Takeda Pharmaceutical. T.M. also received unrestricted research grant for Department of Cardiology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine from Astellas Pharma, Daiichi-Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Kowa, MSD, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharma, Otsuka Pharma, Pfizer Japan, Sanofi-aventis, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Teijin Pharma. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of objective nutritional indexes as predictors of worse outcomes in peritoneal dialysis patients.Nutrition. 2020 Nov-Dec;79-80:110963. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110963. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Nutrition. 2020. PMID: 33011471
-
Prognostic significance of serum cholinesterase in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a prospective comparative study with other nutritional indices.Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Aug 1;110(2):330-339. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqz103. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31161211
-
The prognostic impact of malnutrition in patients with severely decompensated acute heart failure, as assessed using the Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score.Heart Vessels. 2018 Feb;33(2):134-144. doi: 10.1007/s00380-017-1034-z. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Heart Vessels. 2018. PMID: 28803356
-
Assessing the nutritional status of hospitalized elderly.Clin Interv Aging. 2017 Oct 4;12:1615-1625. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S140859. eCollection 2017. Clin Interv Aging. 2017. PMID: 29042762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of composite objective nutritional indexes in patients with chronic kidney disease.Front Nutr. 2024 Apr 18;11:1349876. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1349876. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38699544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value of Cheyne-Stokes Respiration and Nutritional Status in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 15;15(4):964. doi: 10.3390/nu15040964. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839321 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Effect of a Novel Simply Calculated Nutritional Index in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure.Nutrients. 2020 Oct 29;12(11):3311. doi: 10.3390/nu12113311. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33137941 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Obesity and Prognostic Nutritional Index on 1-Year Mortality in Patients with Acute Heart Failure.Card Fail Rev. 2025 Feb 19;11:e03. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2024.35. eCollection 2025. Card Fail Rev. 2025. PMID: 40083652 Free PMC article.
-
Preprocedural Controlling Nutritional Status Score as a Predictor of Mortality in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Mitral Valve Repair - A Single Center Experience in Japan.Circ Rep. 2023 Dec 2;5(12):442-449. doi: 10.1253/circrep.CR-23-0055. eCollection 2023 Dec 8. Circ Rep. 2023. PMID: 38073869 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the adequacy of geriatric nutritional risk index with that of the mini nutritional assessment-short form and global leadership initiative on malnutrition criteria in assessing nutritional status to predict the 1-year prognosis of hospitalized Japanese older adults: a single-institutional cohort study.BMC Geriatr. 2023 Jan 20;23(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-03740-5. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 36670357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bleumink GS, Knetsch AM, Sturkenboom MC, Straus SM, Hofman A, Deckers JW, et al.. Quantifying the heart failure epidemic: Prevalence, incidence rate, lifetime risk and prognosis of heart failure The Rotterdam Study. Eur Heart J 2004; 25: 1614–1619. - PubMed
-
- Okura Y, Ramadan MM, Ohno Y, Mitsuma W, Tanaka K, Ito M, et al.. Impending epidemic: Future projection of heart failure in Japan to the year 2055. Circ J 2008; 72: 489–491. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Negassa A, Afzal R, Poole-Wilson PA, Cohn JN, Yusuf S.. Prognostic importance of weight loss in chronic heart failure and the effect of treatment with angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors: An observational study. Lancet 2003; 361: 1077–1083. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosy AP, Vaduganathan M, Huffman MD, Khan S, Kwasny MJ, Fought AJ, et al.. Clinical course and predictive value of liver function tests in patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: An analysis of the EVEREST trial. Eur J Heart Fail 2012; 14: 302–311. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
