Efficacy of Complex Fractionated Atrial Electrogram-Guided Extensive Encircling Pulmonary Vein Isolation for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 33693139
- PMCID: PMC7889480
- DOI: 10.1253/circrep.CR-19-0002
Efficacy of Complex Fractionated Atrial Electrogram-Guided Extensive Encircling Pulmonary Vein Isolation for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
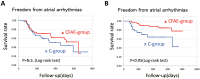
Background: In persistent AF, the effect of adjunctive ablation in addition to PV isolation (PVI) is controversial. We considered a new modified PVI including complex fractionated atrial electrogram (CFAE) area. Methods and Results: In 57 patients with persistent AF undergoing first ablation, CFAE were mapped before ablation and CFAE-guided extensive encircling PVI (CFAE-guided EEPVI) was performed. The PVI line was designed to include the CFAE area near PV or to cross the minimum cycle length points of the CFAE area near PV (CFAE-guided EEPVI group). The outcome was compared with conventional PVI in 34 patients with persistent AF (conventional PVI group). During a mean follow-up of 365±230 days after the first procedure, AF in 13 and atrial tachycardia (AT) in 9 patients recurred in the CFAE-guided EEPVI group, while only AF in 17 patients recurred in the conventional PVI group. Eight of 9 AT in the CFAE-guided EEPVI group were successfully ablated at second procedure. After first and second procedures, the recurrence of atrial tachyarrhythmia in the CFAE-guided EEPVI group was significantly reduced compared with the conventional PVI group (8 patients, 14% vs. 11 patients, 32%, respectively; P<0.01, log-rank test). Conclusions: CFAE-guided EEPVI was more effective for persistent AF compared with conventional PVI after first and second procedures, because recurring AT as well as re-conduction of PV was successfully ablated.
Keywords: Atrial tachycardia; Complex fractionated atrial electrogram; Persistent atrial fibrillation; Pulmonary vein isolation; Radiofrequency catheter ablation.
Copyright © 2019, THE JAPANESE CIRCULATION SOCIETY.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, Takahashi A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, et al.. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: 659–666. - PubMed
-
- Jaïs P, Hocini M, Hsu LF, Sanders P, Scavee C, Weerasooriya R, et al.. Technique and results of linear ablation at the mitral isthmus. Circulation 2004; 110: 2996–3002. - PubMed
-
- Nademanee K, McKenzie J, Kosar E, Scwab M, Sunsaneewitayakul B, Vasavakul T, et al.. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004; 43: 2044–2053. - PubMed
-
- Li WJ, Bai YY, Zhang HY, Tang RB, Miao CL, Sang CH, et al.. Additional ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms after pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2011; 4: 143–148. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
