Identifying Clinical and Genomic Features Associated With Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 33693411
- PMCID: PMC7931938
- DOI: 10.3389/fdata.2020.528828
Identifying Clinical and Genomic Features Associated With Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
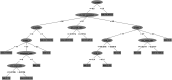
We apply a pattern-based classification method to identify clinical and genomic features associated with the progression of Chronic Kidney disease (CKD). We analyze the African-American Study of Chronic Kidney disease with Hypertension dataset and construct a decision-tree classification model, consisting 15 combinatorial patterns of clinical features and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), seven of which are associated with slow progression and eight with rapid progression of renal disease among African-American Study of Chronic Kidney patients. We identify four clinical features and two SNPs that can accurately predict CKD progression. Clinical and genomic features identified in our experiments may be used in a future study to develop new therapeutic interventions for CKD patients.
Keywords: AASK; chronic kidney disease; classification; decision trees; genomic analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Moreno, Bain, Moreno, Carroll, Cunningham, Ashton, Poteau, Subasi, Lipkowitz and Subasi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
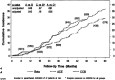
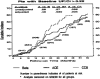
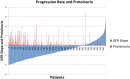
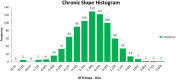


References
-
- Bakris G. L., Weir M. R., Shanifar S., Zhang Z., Douglas J., van Dijk D. J., et al. (2003). Effects of blood pressure level on progression of diabetic nephropathy: results from the RENAAL studyEffects of intensive blood-pressure lowering and low-dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 163, 1555–1565. 10.1001/archinte.163.13.1555 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

