A nanoscale genosensor for early detection of COVID-19 by voltammetric determination of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) sequence of SARS-CoV-2 virus
- PMID: 33694010
- PMCID: PMC7946404
- DOI: 10.1007/s00604-021-04773-6
A nanoscale genosensor for early detection of COVID-19 by voltammetric determination of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) sequence of SARS-CoV-2 virus
Abstract
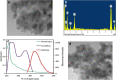
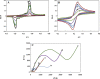
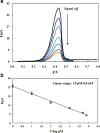
A voltammetric genosensor has been developed for the early diagnosis of COVID-19 by determination of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) sequence as a specific target of novel coronavirus. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) uses an RdRP for the replication of its genome and the transcription of its genes. Here, the silver ions (Ag+) in the hexathia-18-crown-6 (HT18C6) were used for the first time as a redox probe. Then, the HT18C6(Ag) incorporated carbon paste electrode (CPE) was further modified with chitosan and PAMAM dendrimer-coated silicon quantum dots (SiQDs@PAMAM) for immobilization of probe sequences (aminated oligonucleotides). The current intensity of differential pulse voltammetry using the redox probe was found to decrease with increasing the concentration of target sequence. Based on such signal-off trend, the proposed genosensor exhibited a good linear response to SARS-CoV-2 RdRP in the concentration range 1.0 pM-8.0 nM with a regression equation I (μA) = - 6.555 log [RdRP sequence] (pM) + 32.676 (R2 = 0.995) and a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.3 pM. The standard addition method with different spike concentrations of RdRP sequence in human sputum samples showed a good recovery for real sample analysis (> 95%). Therefore, the developed voltammetric genosensor can be used to determine SARS-CoV-2 RdRP sequence in sputum samples. PAMAM-functionalized SiQDs were used as a versatile electrochemical platform for the SARS-CoV-2 RdRP detection based on a signal off sensing strategy. In this study, for the first time, the silver ions (Ag+) in the hexathia-18-crown-6 carrier were applied as an electrochemical probe.
Keywords: Genosensor; PAMAM@SiQDs; SARS-CoV-2 RdRP sequence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Voltammetric-based immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 May 26;188(6):199. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04867-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34041585 Free PMC article.
-
Graphite nanocrystals coated paper-based electrode for detection of SARS-Cov-2 gene using DNA-functionalized Au@carbon dot core-shell nanoparticles.Microchem J. 2022 Aug;179:107585. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2022.107585. Epub 2022 May 11. Microchem J. 2022. PMID: 35578710 Free PMC article.
-
An electrochemical nano-genosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection utilizing Ce-metal organic framework, dendritic palladium nano-structure, and sulfur-doped graphene oxide.Talanta. 2025 May 15;287:127662. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2025.127662. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Talanta. 2025. PMID: 39884121
-
Entropy-driven amplified electrochemiluminescence biosensor for RdRp gene of SARS-CoV-2 detection with self-assembled DNA tetrahedron scaffolds.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Apr 15;178:113015. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113015. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33493896 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Molecular Diagnosis of COVID-19 by the Novel, Highly Sensitive and Specific COVID-19-RdRp/Hel Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR Assay Validated In Vitro and with Clinical Specimens.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Apr 23;58(5):e00310-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00310-20. Print 2020 Apr 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32132196 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Batteryless wireless magnetostrictive Fe30Co70/Ni clad plate for human coronavirus 229E detection.Sens Actuators A Phys. 2023 Jan 1;349:114052. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2022.114052. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Sens Actuators A Phys. 2023. PMID: 36447950 Free PMC article.
-
A review on corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): current progress, clinical features and bioanalytical diagnostic methods.Mikrochim Acta. 2022 Feb 14;189(3):103. doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05167-y. Mikrochim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35157153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel approaches for rapid detection of COVID-19 during the pandemic: A review.Anal Biochem. 2021 Dec 1;634:114362. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2021.114362. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Anal Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34478703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in PCR-free nucleic acid detection for SARS-COV-2.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 7;10:999358. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.999358. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36277389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AuNP-based biosensors for the diagnosis of pathogenic human coronaviruses: COVID-19 pandemic developments.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022 Oct;414(24):7069-7084. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-04193-2. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35781591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
