Efficacy and Safety of Ertugliflozin in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled by Sulfonylurea Monotherapy: a Substudy of VERTIS CV
- PMID: 33694093
- PMCID: PMC7994479
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-021-01018-w
Efficacy and Safety of Ertugliflozin in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled by Sulfonylurea Monotherapy: a Substudy of VERTIS CV
Abstract
Introduction: Sulfonylureas (SU) are commonly used antihyperglycemic agents. VERTIS CV was the cardiovascular outcome study for the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor ertugliflozin. Enrollment of patients in VERTIS CV occurred in two sequential cohorts (Cohort 1 and Cohort 2).
Methods: This substudy assessed the efficacy and safety of adding ertugliflozin to SU monotherapy. The primary endpoint was the change in HbA1c from baseline at 18 weeks.
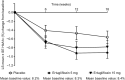
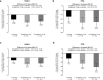
Results: Among the 8246 patients who were randomized in VERTIS CV, 157 patients in Cohort 1 and 135 patients in Cohort 2 were on SU monotherapy at baseline. In the prespecified analysis (Cohort 1 only), the least squares (LS) mean HbA1c change from baseline for placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg was - 0.56%, - 0.91%, and - 0.78%, respectively (placebo-adjusted LS mean [95% CI] change: - 0.35% [- 0.72%, 0.02%]; - 0.22% [- 0.60%, 0.16%] for ertugliflozin 5 and 15 mg, respectively; p > 0.05 for both). In a post-hoc analysis that included Cohorts 1 and 2 (N = 292), the LS mean HbA1c change from baseline at week 18 for placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg was - 0.31%, - 0.77%, and - 0.68%, respectively (placebo-adjusted change: - 0.46% [- 0.73%, - 0.18%]; - 0.37% [- 0.66%, - 0.09%]; p = 0.001 and 0.01 for ertugliflozin 5 and 15 mg, respectively). In Cohort 1, adverse events were reported in 45.8%, 47.3%, and 25.9% of patients with placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg. The incidence rates of symptomatic hypoglycemia were 0.0%, 5.5%, and 3.7%, respectively, with no cases of severe hypoglycemia. The safety profile was similar for Cohorts 1 and 2 combined.
Conclusion: The addition of ertugliflozin to SU monotherapy reduced HbA1c but did not result in significant placebo-adjusted reductions from baseline according to the prespecified primary analysis (n = 157); however, in a post-hoc analysis with a larger patient population (n = 292), significant and clinically relevant HbA1c reductions were observed. Ertugliflozin was generally well tolerated.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01986881.
Keywords: Glycemic; HbA1c; SGLT2 inhibitor; Secondary prevention; Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43:S98-S110. - PubMed
-
- Roglic G, Norris SL. Medicines for treatment intensification in type 2 diabetes and type of insulin in type 1 and type 2 diabetes in low-resource settings: synopsis of the World Health Organization Guidelines on second- and third-line medicines and type of insulin for the control of blood glucose levels in nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:394–397. doi: 10.7326/M18-1149. - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

