Th17, rather than Th1 cell proportion, is closely correlated with elevated disease severity, higher inflammation level, and worse prognosis in sepsis patients
- PMID: 33704828
- PMCID: PMC8128311
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23753
Th17, rather than Th1 cell proportion, is closely correlated with elevated disease severity, higher inflammation level, and worse prognosis in sepsis patients
Abstract
Objective: The current study aimed to investigate the prognostic value of T helper (Th) 1 and Th17 proportions in sepsis patients.
Methods: Th1 and Th17 cells in blood CD4+ T cells were detected by flow cytometry in 210 sepsis patients and 100 healthy controls (HCs). Besides, serum interferon-γ (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-17 (IL-17) levels in the enrolled sepsis patients were determined with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
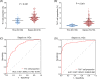
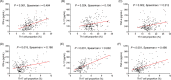
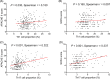
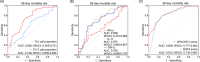
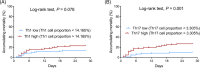
Results: Compared with HCs, Th1 and Th17 proportions were elevated in sepsis patients (both p < .001). Meanwhile, Th1 proportion was strongly correlated with IFN-γ (p < .001, r = .484) but weakly correlated with TNF-α (p = .024, r = .156) and IL-17 (p = .002, r = .212), while Th17 proportion showed faint correlation with IFN-γ (p = .015, r = .168), but strong correlations with TNF-α (p < .001, r = .602) and IL-17 (p < .001, r = .498) in sepsis patients. Besides, Th1 proportion was weakly associated with APACHE II score (p = .030, r = .150), but Th17 proportion was closely associated with APACHE II score (p < .001, r = .322) and SOFA score (p < .001, r = .337) in sepsis patients. Regarding their prognostic value, Th1 proportion (p = .042) was slightly, while Th17 proportion (p < .001) was dramatically, increased in septic deaths compared with survivors, and Th17 possessed good predictive value for 28-day mortality risk (AUC: 0.748, 95% CI: 0.659-0.836).
Conclusion: Th1 and Th17 proportions are elevated in sepsis patients compared with HCs, and Th17 proportion is correlated with increased disease severity, higher inflammation level, and worse prognosis in sepsis patients.
Keywords: 28-day mortality; Comprehensive disease severity scale; Sepsis; Th1; Th17.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M, et al. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet. 2018;392(10141):75‐87. - PubMed
-
- Tiru B, DiNino EK, Orenstein A, et al. The economic and humanistic burden of severe sepsis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2015;33(9):925‐937. - PubMed
-
- Verdonk F, Blet A, Mebazaa A. The new sepsis definition: limitations and contribution to research and diagnosis of sepsis. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2017;30(2):200‐204. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

