Next-Generation Endocrine Therapies for Breast Cancer
- PMID: 33705209
- PMCID: PMC8274744
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.03565
Next-Generation Endocrine Therapies for Breast Cancer
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
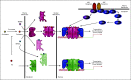
References
-
- Jensen EV, Jacobson HI.Basic guides to the mechanism of estrogen action Rec Prog Horm Res 18387–4141962
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

