Understanding intestinal health in nursery pigs and the relevant nutritional strategies
- PMID: 33705620
- PMCID: PMC7961202
- DOI: 10.5713/ab.21.0010
Understanding intestinal health in nursery pigs and the relevant nutritional strategies
Abstract
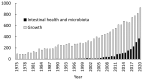
In the modern pig production, pigs are weaned at early age with immature intestine. Dietary and environmental factors challenge the intestine, specifically the jejunum, causing inflammation and oxidative stress followed by destruction of epithelial barrier and villus structures in the jejunum. Crypt cell proliferation increases to repair damages in the jejunum. Challenges to maintain the intestinal health have been shown to be related to changes in the profile of mucosa-associated microbiota in the jejunum of nursery pigs. All these processes can be quantified as biomarkers to determine status of intestinal health related to growth potential of nursery pigs. Nursery pigs with impaired intestinal health show reduced ability of nutrient digestion and thus reduced growth. A tremendous amount of research effort has been made to determine nutritional strategies to maintain or improve intestinal health and microbiota in nursery pigs. A large number of feed additives have been evaluated for their effectiveness on improving intestinal health and balancing intestinal microbiota in nursery pigs. Selected prebiotics, probiotics, postbiotics, and other bioactive compounds can be used in feeds to handle issues with intestinal health. Selection of these feed additives should aim modulating biomarkers indicating intestinal health. This review aims to define intestinal health and introduce examples of nutritional approaches to handle intestinal health in nursery pigs.
Keywords: Inflammation; Intestinal Health; Microbiota; Nursery Pigs; Nutritional Strategies; Oxidative Stress.
Conflict of interest statement
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Cunha TJ, Meadows GB, Edwards HM, Sewell RF, Pearson AM, Glasscock RS. A comparison of aureomycin, streptomycin, penicillin and an aureomycin-B12 feed supplement for the pig. Arch Biochem. 1951;30:269–71. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

