Electrochemical diagnostics of infectious viral diseases: Trends and challenges
- PMID: 33706158
- PMCID: PMC7921732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113112
Electrochemical diagnostics of infectious viral diseases: Trends and challenges
Abstract
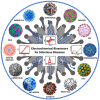
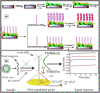
Infectious diseases caused by viruses can elevate up to undesired pandemic conditions affecting the global population and normal life function. These in turn impact the established world economy, create jobless situations, physical, mental, emotional stress, and challenge the human survival. Therefore, timely detection, treatment, isolation and prevention of spreading the pandemic infectious diseases not beyond the originated town is critical to avoid global impairment of life (e.g., Corona virus disease - 2019, COVID-19). The objective of this review article is to emphasize the recent advancements in the electrochemical diagnostics of twelve life-threatening viruses namely - COVID-19, Middle east respiratory syndrome (MERS), Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Influenza, Hepatitis, Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Human papilloma virus (HPV), Zika virus, Herpes simplex virus, Chikungunya, Dengue, and Rotavirus. This review describes the design, principle, underlying rationale, receptor, and mechanistic aspects of sensor systems reported for such viruses. Electrochemical sensor systems which comprised either antibody or aptamers or direct/mediated electron transfer in the recognition matrix were explicitly segregated into separate sub-sections for critical comparison. This review emphasizes the current challenges involved in translating laboratory research to real-world device applications, future prospects and commercialization aspects of electrochemical diagnostic devices for virus detection. The background and overall progress provided in this review are expected to be insightful to the researchers in sensor field and facilitate the design and fabrication of electrochemical sensors for life-threatening viruses with broader applicability to any desired pathogens.
Keywords: COVID-19; Diagnostics; Electrochemical biosensors; Infectious diseases; Point of care (POC); Virus detection.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Algaissi A., Alfaleh M.A., Hala S., Abujamel T.S., Alamri S.S., Almahboub S.A., Alluhaybi K.A., Hobani H.I., Alsulaiman R.M., AlHarbi R.H., ElAssouli M.-Z. ak, Alhabbab R.Y., AlSaieedi A.A., Abdulaal W.H., Al-Somali A.A., Alofi F.S., Khogeer A.A., Alkayyal A.A., Mahmoud A.B., Almontashiri N.A.M., Pain A., Hashem A.M. SARS-CoV-2 S1 and N-based serological assays reveal rapid seroconversion and induction of specific antibody response in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:16561. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73491-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

