Evaluation of whole-body modalities for diagnosis of multifocal osteonecrosis-a pilot study
- PMID: 33706802
- PMCID: PMC7947377
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-021-02473-3
Evaluation of whole-body modalities for diagnosis of multifocal osteonecrosis-a pilot study
Abstract
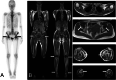
Background: This study aimed to investigate the ability of whole-body bone scintigraphy (WB-BS) in the detection of multifocal osteonecrosis (ON) compared to whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) and to clarify the characteristics of patients with multifocal ON among those with ON of the femoral head (ONFH) using WB-MRI.
Methods: Forty-six patients who had symptomatic ONFH and underwent surgery in our hospital from April 2019 to October 2020 were included in the study. Data on patient demographics, including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), history of corticosteroid intake, alcohol abuse, smoking, and symptomatic joints, were collected from their medical records. All patients underwent WB-MRI and WB-BS before surgery.
Results: The agreement in the detection of ON by WB-MRI vs the uptake lesions by WB-BS in the hip joints was moderate (κ = 0.584), while that in other joints was low (κ < 0.40). Among the 152 joints with ON detected by WB-MRI, 92 joints (60.5%) were symptomatic, and 60 joints (39.5%) were asymptomatic. Twelve out of the 46 (26.0%) patients had multifocal (three or more distinct anatomical sites) ON. Nonetheless, while WB-BS detected symptomatic ON detected by WB-MRI as uptake lesions in 82.6% (76/92) of the joints, asymptomatic ON detected by WB-MRI was detected as uptake lesions in 21.7% (13/60) of the joints. All patients with multifocal ON had a history of steroid therapy, which was significantly higher than that in patients with oligofocal ON (P = 0.035). The patients with a hematologic disease had multifocal ON at a higher rate (P = 0.015).
Conclusions: It might be difficult for WB-BS to detect the asymptomatic ON detected by WB-MRI compared to symptomatic ON. Considering the cost, examination time, and radiation exposure, WB-MRI might be useful for evaluating multifocal ON. Larger longitudinal studies evaluating the benefits of WB-MRI for detecting the risk factors for multifocal ON are required.
Keywords: Osteonecrosis; Steroid; Whole-body bone scintigraphy; Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Expanding diagnostic approach in patients with osteonecrosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 May 25;23(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02533-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34034809 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Matthews AH, Davis DD, Fish MJ, Stitson D: Avascular Necrosis. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL); 2021. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs B. Epidemiology of traumatic and nontraumatic osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978;130:51–67. - PubMed
-
- LaPorte DM, Mont MA, Mohan V, Jones LC, Hungerford DS. Multifocal osteonecrosis. J Rheumatol. 1998;25(10):1968–1974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

