COVID-19: cross-border contact tracing in Germany, February to April 2020
- PMID: 33706859
- PMCID: PMC7953533
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.10.2001236
COVID-19: cross-border contact tracing in Germany, February to April 2020
Abstract
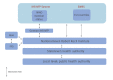
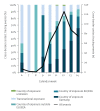
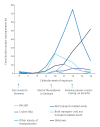
IntroductionThe Robert Koch Institute (RKI) managed the exchange of cross-border contact tracing data between public health authorities (PHA) in Germany and abroad during the early COVID-19 pandemic.AimWe describe the extent of cross-border contact tracing and its challenges.MethodsWe analysed cross-border COVID-19 contact tracing events from 3 February to 5 April 2020 using information exchanged through the European Early Warning Response System and communication with International Health Regulation national focal points. We described events by PHA, number of contacts and exposure context.ResultsThe RKI processed 467 events, initiating contact to PHA 1,099 times (median = 1; interquartile range (IQR): 1-2) and sharing data on 5,099 contact persons. Of 327 (70%) events with known exposure context, the most commonly reported exposures were aircraft (n = 64; 20%), cruise ships (n = 24; 7%) and non-transport contexts (n = 210; 64%). Cruise ship and aircraft exposures generated more contacts with authorities (median = 10; IQR: 2-16, median = 4; IQR: 2-11) and more contact persons (median = 60; IQR: 9-269, median = 2; IQR: 1-3) than non-transport exposures (median = 1; IQR: 1-6 and median = 1; IQR: 1-2). The median time spent on contact tracing was highest for cruise ships: 5 days (IQR: 3-9).ConclusionIn the COVID-19 pandemic, cross-border contact tracing is considered a critical component of the outbreak response. While only a minority of international contact tracing activities were related to exposure events in transport, they contributed substantially to the workload. The numerous communications highlight the need for fast and efficient global outbreak communication channels between PHA.
Keywords: Early Warning and Response System (EWRS) COVID-19; Germany; International Health Regulations; SARS-CoV-2; contact tracing; cross-broader; pandemic preparedness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report – 72. Geneva: WHO: 1 Apr 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2...
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). International Health Regulations (2005). 3rd ed. Geneva: WHO; 2016. Available from: https://www.who.int/ihr/publications/9789241580496/en
-
- European Commission. Decision No 1082/2013/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 October 2013 on serious cross-border threats to health and repealing Decision No 2119/98/EC. Official Journal of the European Union. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. 5 Nov 2013:L 293/1. Available from: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32013D1082
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
