Interrogation of the cellular immunome of cancer patients with regard to the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33707314
- PMCID: PMC7956734
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002087
Interrogation of the cellular immunome of cancer patients with regard to the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
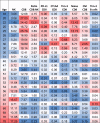
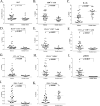
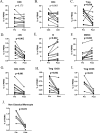
While vaccines directed against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein will have varying degrees of effectiveness in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infections, the severity of infection will be determined by multiple host factors including the ability of immune cells to lyse virus-infected cells. This review will discuss the complexity of both adaptive and innate immunomes and how a flow-based assay can detect up to 158 distinct cell subsets in the periphery. This assay has been employed to show the effect of age on differences in specific immune cell subsets, and the differences in the immunome between healthy donors and age-matched cancer patients. Also reviewed are the numerous soluble factors, in addition to cytokines, that may vary in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infections and may also be employed to help define the effectiveness of a given vaccine or other antiviral agents. Various steroids have been employed in the management of autoimmune adverse events in cancer patients receiving immunotherapeutics and may be employed in the management of SARS-CoV-2 infections. The influence of steroids on multiple immune cells subsets will also be discussed.
Keywords: COVID-19; T-lymphocytes; adaptive immunity; cellular; immunity; immunotherapy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
