Comparison of clinical severity and epidemiological spectrum between coronavirus disease 2019 and influenza in children
- PMID: 33707568
- PMCID: PMC7952543
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85340-0
Comparison of clinical severity and epidemiological spectrum between coronavirus disease 2019 and influenza in children
Abstract
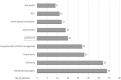
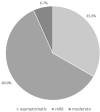
Data on the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children are limited, and studies from Europe are scarce. We analyzed the clinical severity and epidemiologic aspects of COVID-19 in consecutive children aged 0-18 years, referred with a suspicion of COVID-19 between February 1, and April 15, 2020. RT-PCR on a nasopharyngeal swab was used to confirm COVID-19. 319 children met the criteria of a suspected case. COVID-19 was diagnosed in 15/319 (4.7%) patients (8 male; mean age 10.5 years). All of them had household contact with an infected relative. Five (33.3%) patients were asymptomatic. In 9/15 (60.0%) children, the course of the disease was mild, and in 1/15 (6.7%), it was moderate, with the following symptoms: fever (46.7%), cough (40%), diarrhea (20%), vomiting (13.3%), rhinitis (6.7%), and shortness of breath (6.7%). In the COVID-19-negative patients, other infections were confirmed, including influenza in 32/319 (10%). The clinical course of COVID-19 and influenza differed significantly based on the clinical presentation. In conclusion, the clinical course of COVID-19 in children is usually mild or asymptomatic. In children suspected of having COVID-19, other infections should not be overlooked. The main risk factor for COVID-19 in children is household contact with an infected relative.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Situation report-51. Geneva (Switzerland), World Health Organization. 2020; [cited 2020 Mar 12]. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous