The Effects of Luminescent CdSe Quantum Dot-Functionalized Antimicrobial Peptides Nanoparticles on Antibacterial Activity and Molecular Mechanism
- PMID: 33707943
- PMCID: PMC7943780
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S295928
The Effects of Luminescent CdSe Quantum Dot-Functionalized Antimicrobial Peptides Nanoparticles on Antibacterial Activity and Molecular Mechanism
Abstract
Background: With the development of bacterial resistance, the range of effective antibiotics is increasingly becoming more limited. The effective use of nanoscale antimicrobial peptides (AP) in therapeutic and diagnostic methods is a strategy for new antibiotics.
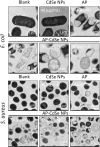
Methods: Combining both AP and cadmium selenide (CdSe) into a composite material may result in a reagent with novel properties, such as enhanced antibacterial activity, fluorescence and favorable stability in aqueous solution.
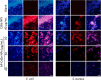
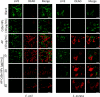
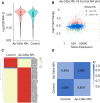
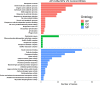
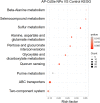
Results: AP-loaded CdSe NPs (AP-CdSe NPs) showed strong antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant (MDR) Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) in vitro and in vivo. Colony-forming unit (CFU) and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) assays showed that AP-CdSe NPs have highly effective antibacterial activity. The quantitative analysis of apoptosis by flow cytometry analysis further confirmed that MDR E. coli and S. aureus treated with AP-CdSe NPs had death rates of 98.76% and 99.13%, respectively. Also, AP-CdSe NPs was found to inhibit bacterial activity in an in vivo bacteremia model in mice infected with S. aureus. In addition, the antibacterial mechanism of AP-CdSe NPs was determined by RNA sequencing analysis. Gene ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis revealed the molecular mechanism of the antibacterial effect of AP-CdSe NPs. Importantly, histopathology analysis, and hematological toxicity analysis indicated that AP-CdSe NPs had few side effects.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that AP loaded on CdSe NPs had a higher water solubility, bioavailability and antibacterial effect compared with raw AP. This study reports findings that are helpful for the design and development of antibacterial treatment strategies based on AP.
Keywords: CdSe QD; RNASeq; antibacterial mechanism; antibacterial peptides; in vitro and in vivo.
© 2021 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there are no competing interests in this work.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

