Biological Function of HYOU1 in Tumors and Other Diseases
- PMID: 33707955
- PMCID: PMC7943547
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S297332
Biological Function of HYOU1 in Tumors and Other Diseases
Abstract
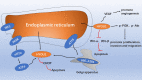
Various stimuli induce an unfolded protein response to endoplasmic reticulum stress, accompanied by the expression of endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperones. Hypoxia-upregulated 1 gene (HYOU1) is a chaperone protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum. HYOU1 expression was upregulated in many diseases, including various cancers and endoplasmic reticulum stress-related diseases. HYOU1 does not only play an important protective role in the occurrence and development of tumors, but also is a potential therapeutic target for cancer. HYOU1 may also be used as an immune stimulation adjuvant because of its anti-tumor immune response, and a molecular target for therapy of many endoplasmic reticulum-related diseases. In this article, we summarize the updates in HYOU1 and discuss the potential therapeutic effects of HYOU1.
Keywords: HYOU1; anti-tumor immunity; endoplasmic reticulum; tumor.
© 2021 Rao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- da Silva DC, Valentao P, Andrade PB, Pereira DM. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders: tools and strategies to understand its complexity. Pharmacol Res. 2020;155:104702. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

