Validation of Microbiological Testing of Tissue Preparations with Different Incubation Temperatures
- PMID: 33708049
- PMCID: PMC7923897
- DOI: 10.1159/000513646
Validation of Microbiological Testing of Tissue Preparations with Different Incubation Temperatures
Abstract
Introduction: The European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) provides principles for microbiological testing of tissue preparations. According to the Ph. Eur., tests should be performed at different temperatures for detection of aerobic bacteria and fungi (20-25°C) vs. anaerobic bacteria (30-35°C). Semiautomated systems using blood culture bottles are already widely used and they are adequate for growth detection. Resin-containing bottles and the addition of penicillinase permit testing of culture media containing antibiotics.
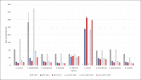
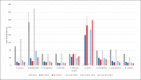
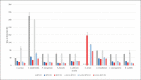
Materials and methods: At 3 temperatures (21, 30, and 35°C) cornea culture media with and without dextran (CM II and CM I) and thermal disinfected femoral head medium (FH) were spiked with the 6 reference strains recommended by the Ph. Eur. (additionally: Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Cutibacterium acnes). Microbial growth was monitored with the BACTECTM FX unit or visually at 21°C.
Results: Growth for all strains was detected with each medium at all 3 temperatures, except for C. acnes at 21°C (all media) and 30°C with FH. C. acnes had the highest times to detection, requiring test durations of 14 days. Microbial growth was faster at 30 and 35°C compared to 21°C.
Conclusion: The requirements according to the Ph. Eur. for a successful method suitability test could be fulfilled for the semiautomated blood culture bottle system with the BACTECTM FX unit for the media and microorganisms used. In the presented validation study 35°C was shown to be the incubation temperature with the fastest growth, of the majority of the test strains used, and complete detection within 14 days.
Keywords: BACTECTM FX; Cornea; Femoral head; Microbiological testing; Temperature; Tissue preparations.
Copyright © 2020 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Schroeter J, Maier P, Bednarz J, Bluthner K, Quenzel M, Pruss A, et al. Procedural guidelines. Good tissue practice for cornea banks. Ophthalmologe. 2009;106((3)):265–74. 76. - PubMed
-
- Pruss A, Göbel UB, Pauli G. Infections associated with musculoskeletal-tissue allografts. N Engl J Med. 2004 Sep;351((13)):1358–60. - PubMed
-
- Kainer MA, Linden JV, Whaley DN, Holmes HT, Jarvis WR, Jernigan DB, et al. Clostridium infections associated with musculoskeletal-tissue allografts. N Engl J Med. 2004 Jun;350((25)):2564–71. - PubMed
-
- Kuehnert MJ, Clark E, Lockhart SR, Soll DR, Chia J, Jarvis WR. Candida albicans endocarditis associated with a contaminated aortic valve allograft: implications for regulation of allograft processing. Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Oct;27((4)):688–91. - PubMed
-
- Wilson ML. Blood cultures. Introduction. Clin Lab Med. 1994 Mar;14((1)):1–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

