Astragaloside IV Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats by Regulating Inflammatory Factors Level via TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33708118
- PMCID: PMC7941269
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.605064
Astragaloside IV Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats by Regulating Inflammatory Factors Level via TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
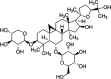
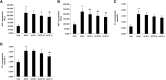
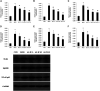
Objective: Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is the primary bioactive component purified from Astragalus membranaceus which is one of the traditional Chinese medicines. Research studies found that AS-IV has significant pharmacological effects on focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease, liver cirrhosis, and diabetic nephropathy, but little is known about the effects of AS-IV on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In this study, we investigated whether AS-IV has beneficial effects on NAFLD in rats and its potential mechanisms. Methods: Male SD rats were fed with high-fat diet (HFD) for 12 weeks to establish NAFLD rat model, and then, the rats were divided into five groups. The control group rats were fed with normal diet for 12 weeks and then were given normal saline (1.0 ml kg-1 day-1) by intragastric administration for 4 weeks. The model group rats were fed with HFD for 12 weeks and then were given normal saline (1.0 ml kg-1 day-1) by intragastric administration for 4 weeks. The AS-IV-L, AS-IV-M, and AS-IV-H groups were treated with 20, 40, and 80 mg kg-1 day-1 of AS-IV by intragastric administration for 4 weeks and given HFD diet. Then, we detected serum transaminase (ALT, AST), blood lipid (TG, TC), inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α), liver histology(NAFLD activity score), TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in liver tissue. Results: We found AS-IV significantly reduced serum levels of AST, ALT, TG, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 in NAFLD rats and downregulate the expression of TLR4 mRNA, MyD88 mRNA, NF-κB mRNA, and proteins in liver tissue. Moreover, AS-IV could significantly reduce the NAFLD activity score of NAFLD rat liver. Conclusion: In this study, we demonstrated that AS-IV have a protective effect on NAFLD by inhibiting TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 levels and down-regulating TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB expression in rat liver tissues.
Keywords: astragaloside IV; myeloid differentiation factor 88; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; nuclear factor-kappa B; toll like receptor 4.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Zhang, Wang, Fu, Han, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


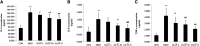
Similar articles
-
Berberine inhibits liver damage in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2020 Dec;31(12):902-909. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2020.19568. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33626003 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of catgut embedding at back-shu points for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis based on IKK/IKB/NF-κB signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2020 Jan 12;40(1):59-66. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20181204-0002. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2020. PMID: 31930901 Chinese.
-
Alleviation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by Huazhi Fugan Granules is associated with suppression of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2021 Sep-Oct;33(5):257-266. doi: 10.1016/j.arteri.2020.12.007. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Clin Investig Arterioscler. 2021. PMID: 33810882 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Astragaloside IV prevents acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Food Biochem. 2021 Jul;45(7):e13757. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13757. Epub 2021 May 25. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34032295
-
Pharmacological Effects and Molecular Protective Mechanisms of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 3;13:854674. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.854674. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35308224 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: A study-level pooled analysis of 44 randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1009571. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1009571. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36313382 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside IV regulates autophagy-mediated proliferation and apoptosis in a rat model of PCOS by activating the PPARγ pathway.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Jul;25(7):882-889. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.64475.14179. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36033957 Free PMC article.
-
CS27109, A Selective Thyroid Hormone Receptor-β Agonist Alleviates Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Murine Models.Int J Endocrinol. 2023 Feb 14;2023:4950597. doi: 10.1155/2023/4950597. eCollection 2023. Int J Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 36825196 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte-Conditional Knockout of Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein 4 Aggravated LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Injury via the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 8;13:901566. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.901566. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35874667 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential and mechanistic insights of astragaloside IV in the treatment of arrhythmia: a comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 10;16:1528208. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1528208. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40276608 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chalasani N., Younossi Z., Lavine J. E., Diehl A. M., Brunt E. M., Cusi K., et al. (2012). The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of liver diseases, American College of gastroenterology, and the American gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 55, 2005–2023. 10.1002/hep.25762 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Csak T., Velayudham A., Hritz I., Petrasek J., Levin I., Lippai D., et al. (2011). Deficiency in myeloid differentiation factor-2 and toll-like receptor 4 expression attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 300, G433–G441. 10.1152/ajpgi.00163.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

