Social Support and Cognition: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33708164
- PMCID: PMC7941073
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.637060
Social Support and Cognition: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Although the influence of social support in health is a widely acknowledged factor, there is a significant gap in the understanding of its role on cognition. The purpose of this systematic review was, therefore, to determine the state-of-the-art on the literature testing the association between social support and cognition. Using six databases (WoS, PubMed, ProQuest, PsycINFO, Scopus and EBSCOhost), we identified 22 articles published between 1999 and 2019 involving an empirical quantitative focus which meet the inclusion criteria. Data extraction was performed following PRISMA recommendations. To summarize the extracted data, we used a narrative synthesis approach. Despite limitations, there is overall preliminary evidence of a relevant positive association between social support and cognition. Our results demonstrate there is enough information for an outbreak of experimental research in the area and an expansion of this body of knowledge. We argue that the present evidence lays the foundations for a more comprehensive theoretical model, one that corresponds with the complexity of the topic and possibly considers models derived from social interaction and active inference theories.
Keywords: cognition; cognitive functioning; cognitive performance; social interaction; social support.
Copyright © 2021 Costa-Cordella, Arevalo-Romero, Parada and Rossi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
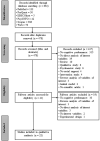


Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Non-familial intergenerational interventions and their impact on social and mental wellbeing of both younger and older people-A mapping review and evidence and gap map.Campbell Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 16;19(1):e1306. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1306. eCollection 2023 Mar. Campbell Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36913218 Free PMC article.
-
The role of family and friends in providing social support towards enhancing the wellbeing of postpartum women: a comprehensive systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011;9(10):313-370. doi: 10.11124/01938924-201109100-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 27819889
-
Effects of caregiver-provided individual cognitive interventions on cognition, social functioning and quality of life in older adults with major neurocognitive disorders: a systematic review.JBI Evid Synth. 2020 Apr;18(4):743-806. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-D-19-00125. JBI Evid Synth. 2020. PMID: 32813340
-
Cognitive Remediation Interventions in Autism Spectrum Condition: A Systematic Review.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Jul 24;11:722. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00722. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32793009 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Examining the association between functional social support, marital status, and memory: a systematic review.BMC Geriatr. 2023 May 12;23(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12877-023-03982-3. BMC Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37173618 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing negative cyber-bystander behavior: A systematic literature review.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 3;10:965017. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.965017. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36262235 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Social Support in an Online Support Community for Tourette Syndrome and Tic Disorders: Analysis of Postings.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Oct 4;24(10):e34403. doi: 10.2196/34403. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 36194454 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions Associated With Reduced Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Oct 3;5(10):e2236676. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.36676. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36251294 Free PMC article.
-
Latent profiles of nurses' subjective well-being and its association with social support and professional self-concept.Nurs Open. 2024 Mar;11(3):e2146. doi: 10.1002/nop2.2146. Nurs Open. 2024. PMID: 38532303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrera M. (1986). Distinctions between social support concepts, measures, and models. Am. J. Community Psychol. 14, 413–445. 10.1007/BF00922627 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

