MAPKAP Kinase-2 Drives Expression of Angiogenic Factors by Tumor-Associated Macrophages in a Model of Inflammation-Induced Colon Cancer
- PMID: 33708191
- PMCID: PMC7940202
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.607891
MAPKAP Kinase-2 Drives Expression of Angiogenic Factors by Tumor-Associated Macrophages in a Model of Inflammation-Induced Colon Cancer
Abstract
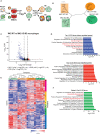
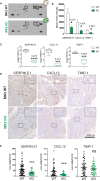
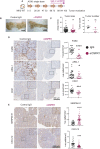
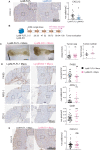
Chronic inflammation increases the risk for colorectal cancer through a variety of mechanisms involving the tumor microenvironment. MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2), a major effector of the p38 MAPK stress and DNA damage response signaling pathway, and a critical regulator of pro-inflammatory cytokine production, has been identified as a key contributor to colon tumorigenesis under conditions of chronic inflammation. We have previously described how genetic inactivation of MK2 in an inflammatory model of colon cancer results in delayed tumor progression, decreased tumor angiogenesis, and impaired macrophage differentiation into a pro-tumorigenic M2-like state. The molecular mechanism responsible for the impaired angiogenesis and tumor progression, however, has remained contentious and poorly defined. Here, using RNA expression analysis, assays of angiogenesis factors, genetic models, in vivo macrophage depletion and reconstitution of macrophage MK2 function using adoptive cell transfer, we demonstrate that MK2 activity in macrophages is necessary and sufficient for tumor angiogenesis during inflammation-induced cancer progression. We identify a critical and previously unappreciated role for MK2-dependent regulation of the well-known pro-angiogenesis factor CXCL-12/SDF-1 secreted by tumor associated-macrophages, in addition to MK2-dependent regulation of Serpin-E1/PAI-1 by several cell types within the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: MAPKAP kinase 2; angiogenesis; colon tumors; inflammation driven tumorigenesis; signal transduction; stress signaling; tumor associated macrophage (TAM).
Copyright © 2021 Suarez-Lopez, Kong, Sriram, Patterson, Rosenberg, Morandell, Haigis and Yaffe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MK2 contributes to tumor progression by promoting M2 macrophage polarization and tumor angiogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 1;115(18):E4236-E4244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1722020115. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29666270 Free PMC article.
-
MK2 Regulates Macrophage Chemokine Activity and Recruitment to Promote Colon Tumor Growth.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 21;9:1857. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01857. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30298062 Free PMC article.
-
EMC10 (Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Protein Complex Subunit 10) Is a Bone Marrow-Derived Angiogenic Growth Factor Promoting Tissue Repair After Myocardial Infarction.Circulation. 2017 Nov 7;136(19):1809-1823. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029980. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28931551
-
Biological functions and role of mitogen-activated protein kinase activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) in inflammatory diseases.Pharmacol Rep. 2017 Aug;69(4):746-756. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.03.023. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Pharmacol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28582691 Review.
-
MK2-TNF-Signaling Comes Full Circle.Trends Biochem Sci. 2018 Mar;43(3):170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Trends Biochem Sci. 2018. PMID: 29275999 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor MK2 transcript levels are associated with improved response to chemotherapy and patient survival in non-small cell lung cancer.Physiol Genomics. 2023 Apr 1;55(4):168-178. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00155.2022. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Physiol Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36878491 Free PMC article.
-
From Structure to Function: How Prebiotic Diversity Shapes Gut Integrity and Immune Balance.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 12;16(24):4286. doi: 10.3390/nu16244286. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39770907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue macrophages: origin, heterogenity, biological functions, diseases and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Mar 7;10(1):93. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02124-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40055311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Proteins in Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Their Applications in Cancers.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 2;12(3):392. doi: 10.3390/biom12030392. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-Specificity Phosphatases in Regulation of Tumor-Associated Macrophage Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 16;24(24):17542. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417542. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

